In the rapidly evolving world of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), engineers and researchers are faced with the crucial decision of choosing between commercial and open-source software solutions. ANSYS Fluent is the industry-leading commercial platform, while OpenFOAM offers a powerful open-source alternative. As highlighted in our previous article “What is ANSYS Fluent?”, both platforms provide unique capabilities for solving complex fluid flow problems. This comparison aims to help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
Contents
ToggleTable 1: Quick Comparison Overview
|
Feature |
ANSYS Fluent |
OpenFOAM |
|
License Type |
Commercial |
Open-source |
|
User Interface |
Integrated GUI |
Command-line/Third-party GUI |
|
Learning Curve |
Moderate | Steep |
| Technical Support | Professional |
Community-based |
|
Code Customization |
Limited | Full access |
|
Cost |
High |
Free |
ANSYS Fluent Vs. OpenFOAM Visualization Features
ANSYS Fluent provides an integrated graphical user interface (GUI) with real-time visualization capabilities, making it particularly user-friendly for beginners. As discussed in our article “ANSYS Fluent vs ANSYS Discovery”, Fluent’s visualization tools are comprehensive and well-integrated. OpenFOAM, on the other hand, relies on third-party visualization tools like ParaView, offering flexibility but requiring additional setup and learning.
Figure 1 illustrates the comparison between the interfaces of OpenFOAM and ANSYS Fluent. The integrated GUI of ANSYS Fluent provides a seamless user experience, allowing for real-time visualization of simulation results. This feature is particularly beneficial for beginners and those who prefer a more intuitive interface. OpenFOAM, while powerful, requires additional setup for visualization, typically using tools like blockMesh. This adds a layer of complexity but also offers greater flexibility for customized visualizations.
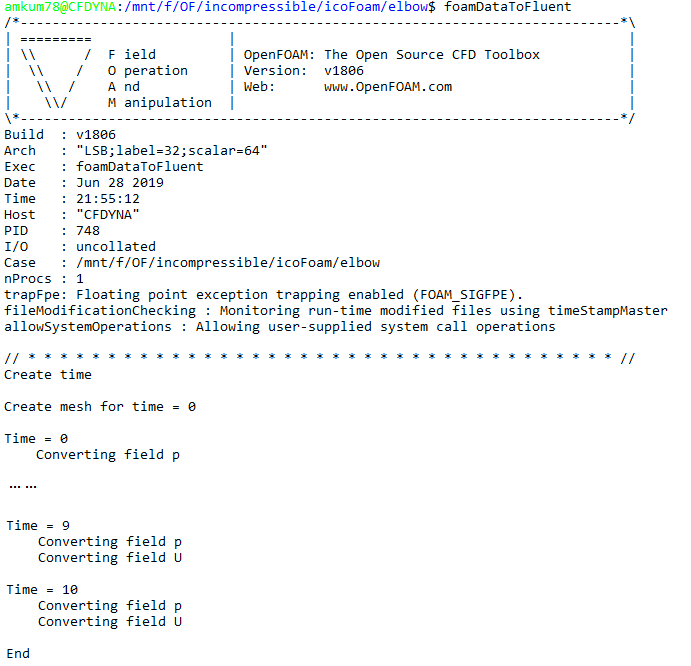
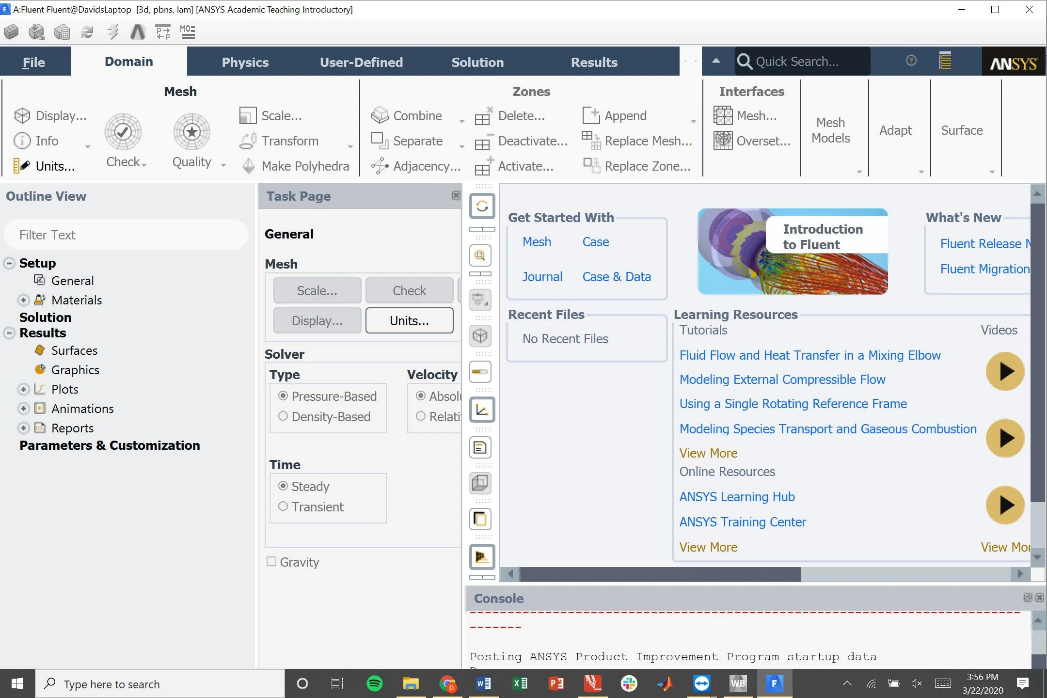
Figure 1: Comparison between the interfaces of OpenFOAM and ANSYS Fluent
The Basis of the Solution Method and Software Code
Both platforms utilize the Finite Volume Method (FVM) for discretization, but their implementations differ significantly. ANSYS Fluent uses a proprietary, closed-source code optimized for commercial applications, while OpenFOAM’s open-source nature allows for complete code customization. As highlighted in our “ANSYS CFX and Fluent” comparison, this difference becomes particularly important when dealing with specialized applications.
Methods Of ANSYS Fluent Vs. OpenFOAM
Both ANSYS Fluent and OpenFOAM provide comprehensive sets of models and solvers for various CFD applications, each with their unique strengths and implementation approaches. OpenFOAM offers specialized solvers such as simpleFoam for incompressible turbulent flows, pimpleFoam for transient incompressible flows, and rhoSimpleFoam for compressible flows. These solvers can be customized and modified according to specific simulation needs, making OpenFOAM highly flexible for specialized applications.
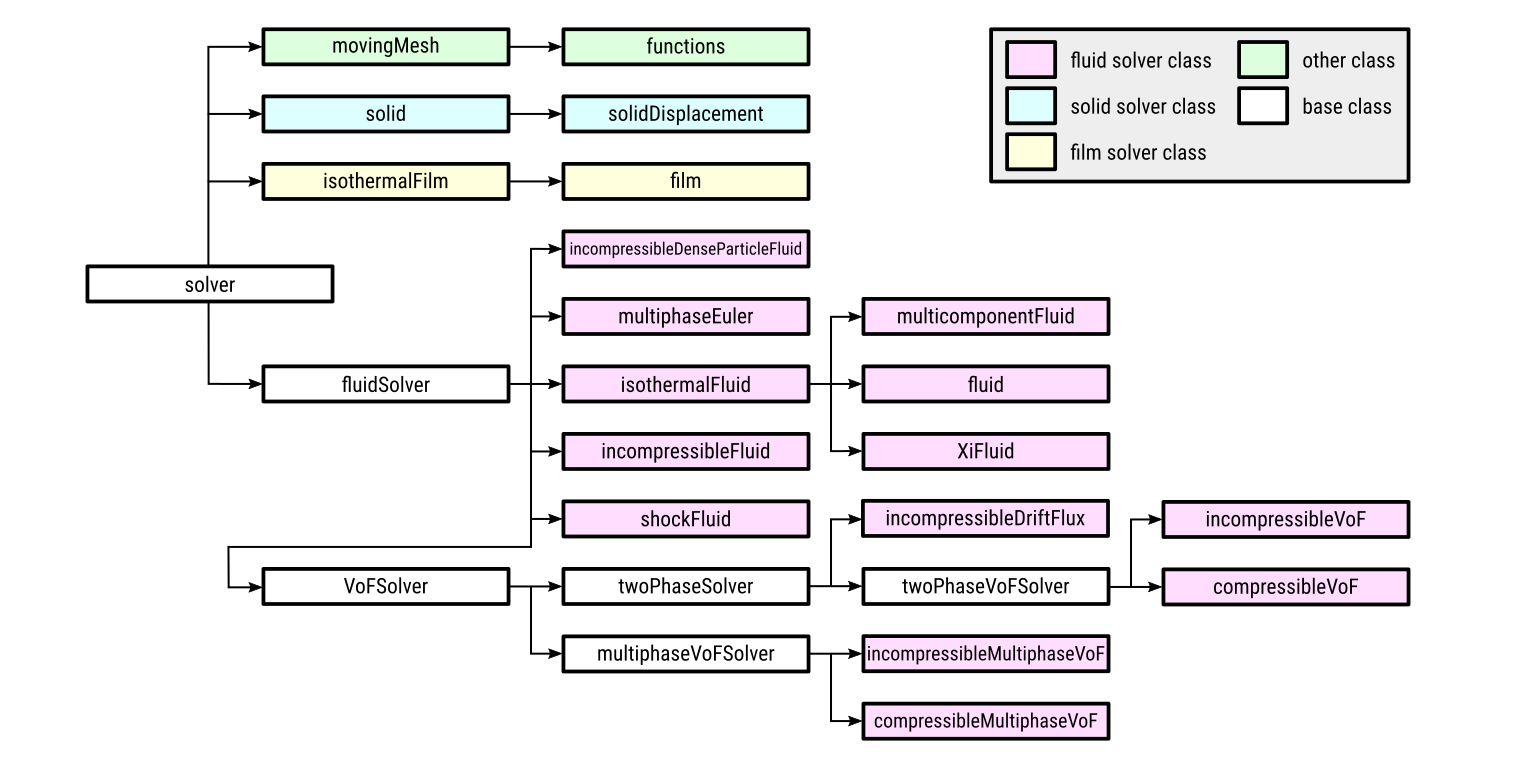
Fig 2. The modular diagram of solvers in OpenFOAM – Resources: https://cfd.direct/openfoam/free-software/modular-solvers/
ANSYS Fluent, on the other hand, provides a more integrated approach with comprehensive modeling capabilities. Its advanced turbulence models, multiphase flow simulations, and heat transfer modeling are optimized for industrial applications. The software includes sophisticated features like custom user-defined functions (UDFs) and specialized models for combustion, acoustics, and battery. As highlighted in our “ANSYS Fluent vs COMSOL” article, Fluent’s implementation of these models is particularly robust and well-validated for complex industrial applications.
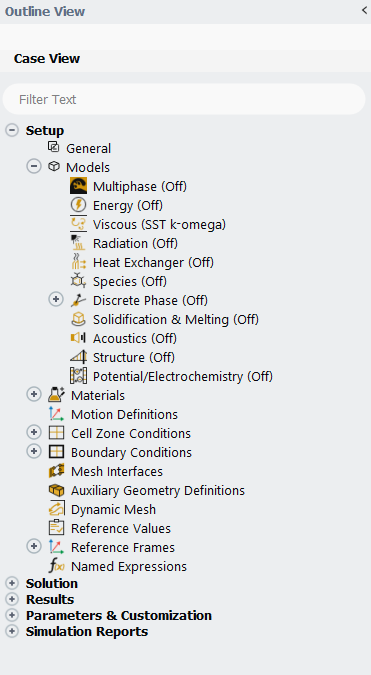
Fig 3. Models available in ANSYS Fluent software
The diversity and implementation of these models reflect the fundamental differences between the two platforms. While OpenFOAM’s open-source nature allows for complete customization and modification of solvers, ANSYS Fluent’s commercial approach provides thoroughly tested, optimized implementations with comprehensive documentation and support. For instance, in turbulent flow simulations, both software packages offer various models, but Fluent’s implementation is often more straightforward to use and validate, particularly for industrial applications. This makes ANSYS Fluent suitable for users who need reliable, well-documented models for standard applications, while OpenFOAM appeals to those requiring highly customized solutions or working on novel applications requiring solver modifications.
Accuracy and Computational Cost
The accuracy and computational cost of both platforms can vary significantly depending on the application. ANSYS Fluent generally offers more advanced algorithms and optimized performance, particularly for complex CFD simulations. However, OpenFOAM’s flexibility and customization capabilities can lead to more tailored and potentially more accurate solutions for specific applications.
The computational cost of OpenFOAM is typically lower due to its open-source nature, but this can come at the expense of longer setup and learning times.
Creating the Geometry, Meshing, and Post-Processing
The approach to geometry creation, meshing, and post-processing differs significantly between ANSYS Fluent and OpenFOAM. ANSYS Fluent provides an integrated workflow within the ANSYS Workbench environment, offering tools like DesignModeler and SpaceClaim for geometry creation, along with sophisticated meshing capabilities that support tetrahedral, hexahedral, and polyhedra cells. As discussed in our article “How to Use ANSYS Fluent?”, this integrated approach streamlines the simulation process, particularly for industrial applications. The software includes built-in mesh quality checking and automated mesh generation features, while post-processing can be performed using specialized tools like CFD-Post and ANSYS EnSight, offering real-time visualization capabilities.
OpenFOAM, in contrast, relies on third-party tools for these crucial steps. Geometry creation typically involves software like FreeCAD or SALOME, while meshing is handled through tools like snappyHexMesh or blockMesh, which support unstructured cells with boundary layers. For post-processing, OpenFOAM users commonly employ ParaView or Tecplot. While this approach requires additional setup and learning time, it offers greater flexibility and customization options.
Fig 4. FreeCAD software vision – Resources: https://i.materialise.com/blog/en/freecad-tutorial-review/

Fig 5. SpaceClaim software vision – Resources: https://www.ansys.com/products/3d-design/ansys-spaceclaim
The mesh quality standards also differ between the platforms – while OpenFOAM has no strict limits on aspect ratio or skewness, ANSYS Fluent enforces specific quality criteria to ensure convergence.
Table 2: Comparison of ANSYS Fluent and OpenFOAM third-party tools
|
Stage |
ANSYS Fluent |
OpenFOAM |
|
Geometry Creation |
– ANSYS DesignModeler – SpaceClaim – Import from: SolidWorks, CATIA |
– FreeCAD |
|
Meshing |
– ANSYS Meshing – SpaceClaim – Supports: tetrahedral, hexahedral, polyhedra cells – Integrated mesh quality checking |
– snappyHexMesh |
|
Post-Processing |
– CFD-Post – ANSYS EnSight – Built-in visualization tools – Real-time visualization |
– ParaView |
Community and Support
Both platforms have extensive communities and support systems, but the nature of this support differs significantly. ANSYS Fluent offers professional technical support and a wide range of tutorials and documentation. On the other hand, OpenFOAM relies on a large and active community-based support system, with numerous forums and user-contributed resources.
Vision of Future
ANSYS has a long history of innovation and continuous development, with a strong focus on integrating advanced algorithms and high-performance computing. OpenFOAM, being open-source, benefits from a large community of contributors who continuously improve and expand its capabilities. Both platforms are expected to continue evolving, with ANSYS likely maintaining its lead in commercial applications and OpenFOAM offering more flexibility for customized solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between ANSYS Fluent and OpenFOAM depends on your specific needs and resources. If you require comprehensive, integrated tools and professional support, ANSYS Fluent is the ideal choice. On the other hand, if you need a flexible, customizable, and cost-effective solution, OpenFOAM offers powerful capabilities with the added benefit of a strong community support system.
At CFDLand, we specialize in conducting CFD projects using ANSYS Fluent. Whether you need expert assistance or want to purchase high-quality CFD simulations, feel free to explore our CFD Project offerings.
FAQs
- What is the main difference between the user interfaces of ANSYS Fluent and OpenFOAM?
- ANSYS Fluent offers an integrated GUI with real-time visualization, while OpenFOAM relies on command-line and third-party GUI tools.
- Which platform is better for customized CFD simulations?
- OpenFOAM offers full access to the source code, making it highly customizable for specialized applications.
- How does the computational cost compare between ANSYS Fluent and OpenFOAM?
- ANSYS Fluent can be more expensive due to its commercial nature, while OpenFOAM is free but may require more setup and learning time.
- What kind of support is available for each platform?
- ANSYS Fluent offers professional technical support, while OpenFOAM relies on community-based support.
- Which platform is better for beginners?
- ANSYS Fluent is generally more user-friendly for beginners due to its integrated GUI and comprehensive documentation.
- What is the future vision for both platforms?
- ANSYS Fluent is expected to continue innovating with advanced algorithms and high-performance computing, while OpenFOAM will benefit from continuous community contributions and flexibility for customized solutions.