Erosion in Air-Cooled Condensers (ACC): A Fluent CFD Simulation Guide
Erosion in Air-Cooled Condensers (ACC): A Fluent CFD Simulation Guide
- Upon ordering this product, you will be provided with a geometry file, a mesh file, and an in-depth Training Video that offers a step-by-step training on the simulation process.
- For any more inquiries regarding the product, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at info@CFDLAND.com or through our online support assistant.
€260 Original price was: €260.€135Current price is: €135.
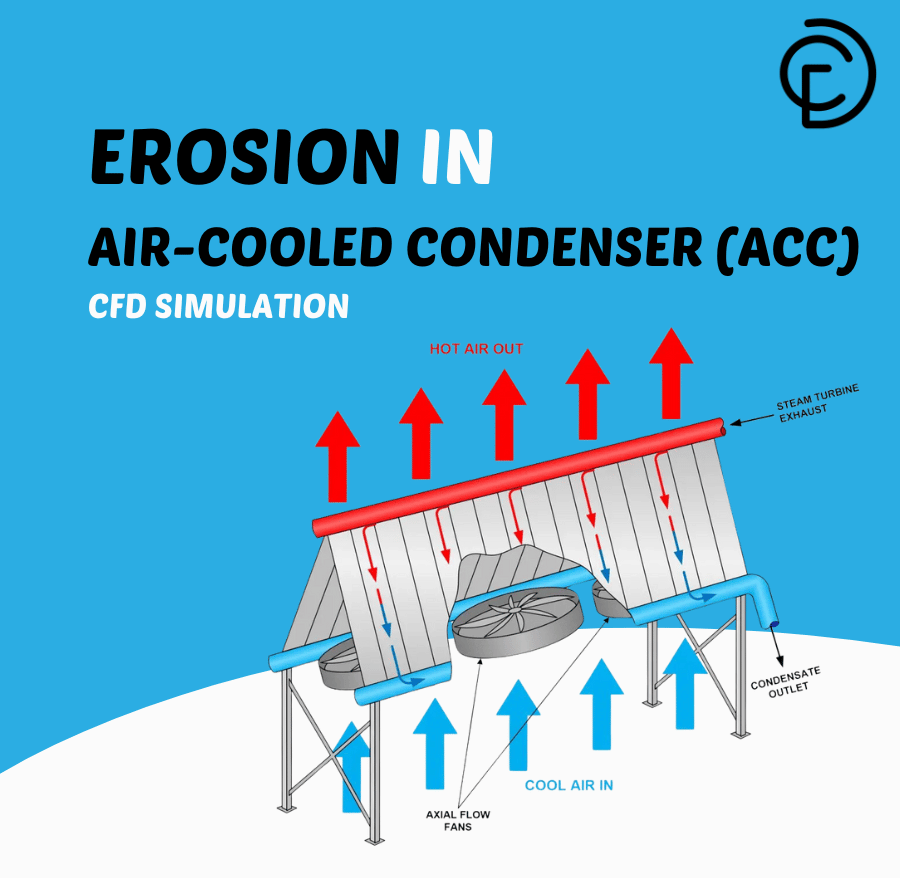
Erosion in air-cooled condensers (ACCs) is a very serious problem for power plants. These ACC systems are essential for cooling in large industrial sites where water is hard to find. The problem happens when fast-moving steam, carrying tiny dust particles or water droplets, hits the metal tubes of the condenser. This constant impact slowly wears away the metal, which is called erosion. This damage can make the tubes thin and weak, possibly causing them to burst. When this happens, the whole cooling system works less efficiently, which wastes energy and lowers the power plant’s output. A good Air-cooled Condenser (ACC) CFD study helps us understand where this damage occurs. By using a special method called the Discrete Phase Model (DPM), we can track these damaging particles. This Erosion Fluent simulation allows engineers to see the erosion patterns and design better, stronger ACCs that last longer and work more efficiently. This study is based on the methods described in a trusted research paper [1].
- Reference [1]: Yang, Lijun, et al. “Thermal-flow characteristics of the new wave-finned flat tube bundles in air-cooled condensers.” International Journal of Thermal Sciences53 (2012): 166-174.

Figure 1: Schematic of the Air-cooled Condenser (ACC) model used for the CFD analysis [1].
Simulation Process: Fluent Modeling, Meshing the Tubes and Defining the Erosion Model
For our Erosion In Air-cooled Condenser (ACC) Fluent simulation, we focused on a single passage of the finned tubes. The detailed geometry was meshed using 936,482 polyhedral cells to create an accurate model. The most important part of this simulation was modeling the sand particles carried by the steam. To do this, we activated the Discrete Phase Model (DPM) in ANSYS Fluent. We set it up as a two-way DPM, which means the software calculates how the particles are pushed by the flow, and also how the particles affect the flow’s movement. To make the particle movement more realistic, we also used the discrete random walk (DRW) model. Even though we only modeled one small part of the condenser, we used periodic boundaries. This smart trick lets the results from this one small section represent the behavior of the entire, much larger system.

Figure 2: Finned tube geometry used in the Air-cooled Condenser (ACC) CFD simulation [1].
Post-processing: CFD Analysis, Visualizing Erosion Hotspots and Thermal Performance
The erosion rate contour provides a clear, professional visual of where the condenser tubes are being damaged. The results show that the erosion is not even. Instead, there are specific hotspots where the damage is much worse. Our simulation found that the peak erosion rate reaches 1.81e-06 kg/m²-s. These high-erosion areas, seen in yellow and red on the contour, are located where the high-speed flow hits the tube surface directly. Most of the tube surface shows very little damage (blue), but these few hotspots are critical because they are the points where a failure is most likely to begin. This professional visual gives engineers the exact information they need to add extra protection only where it is needed most.


Figure 3: DPM Erosion Rate contour from the Erosion Fluent analysis, showing hotspots on the condenser tube.
The temperature contour tells the other half of the story: how well the condenser is cooling. This professional visual shows a clear temperature change as the steam flows through the tubes, dropping from a hot 320K (about 47°C) at the top to a cool 291.9K (about 19°C) at the bottom. This temperature drop of nearly 28 degrees shows that the heat exchanger is successfully removing heat from the steam, which is its main job. By understanding both the erosion risk and the thermal performance, engineers get a complete picture of how the ACC is working. The most important achievement of this simulation is the successful use of a coupled DPM model to accurately pinpoint the locations of maximum erosion while also verifying the condenser’s thermal performance, providing a complete and actionable tool for designing more durable and efficient Air-Cooled Condensers.
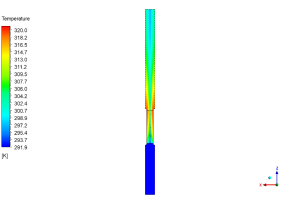
Figure 4:
Temperature distribution from the ACC CFD simulation, showing the effective cooling process.
We pride ourselves on presenting unique products at CFDLAND. We stand out for our scientific rigor and validity. Our products are not based on guesswork or theoretical assumptions like many others. Instead, most of our products are validated using experimental or numerical data from valued scientific journals. Even if direct validation isn’t possible, we build our models and assumptions on the latest research, typically using reference articles to approximate reality.
Yes, we’ll be here . If you have trouble loading files, having technical problems, or have any questions about how to use our products, our technical support team is here to help.
You can load geometry and mesh files, as well as case and data files, using any version of ANSYS Fluent.
€160 Original price was: €160.€80Current price is: €80.

€240 Original price was: €240.€175Current price is: €175.

€295 Original price was: €295.€175Current price is: €175.

€120 Original price was: €120.€65Current price is: €65.

€200 Original price was: €200.€125Current price is: €125.

€240 Original price was: €240.€135Current price is: €135.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.