Dual Savonius Turbines CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Tutorial
Dual Savonius Turbines CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Tutorial
- Upon ordering this product, you will be provided with a geometry file, a mesh file, and an in-depth Training Video that offers a step-by-step training on the simulation process.
- For any more inquiries regarding the product, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at info@CFDLAND.com or through our online support assistant.
€195.00 Original price was: €195.00.€145.00Current price is: €145.00.
The development of renewable energy technologies is greatly aided by the Dual Savonius wind turbine, which stands out by the unique vertical-axis design with two Savonius rotors. This specific type of turbine is noteworthy for its capacity to function effectively at low wind speeds, which makes it appropriate for a variety of urban and rural situations where wind conditions may not be optimal. The Dual Savonius turbine’s characteristics, like its low starting torque and low noise levels, make it a more appealing sustainable energy option. Because they offer important insights into airflow patterns, drag, and lift forces acting on the rotors, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are crucial for maximizing the performance of these turbines. Dual Savonius turbine integration into wind farms can make a substantial contribution to a diversified energy portfolio, improving energy security and lowering dependency on fossil fuels as the demand for renewable energy rises globally. The characteristics of Dual Savonius turbines and the effects of CFD simulations on their efficiency and design will be examined in this research based on a reference paper entitled “Design optimization of an innovative deflector with bleed jets to enhance the performance of dual Savonius turbines using CFD-Taguchi method”.
- Reference [1]: Fatahian, Hossein, et al. “Design optimization of an innovative deflector with bleed jets to enhance the performance of dual Savonius turbines using CFD-Taguchi method.” Energy Conversion and Management 296 (2023): 117655.
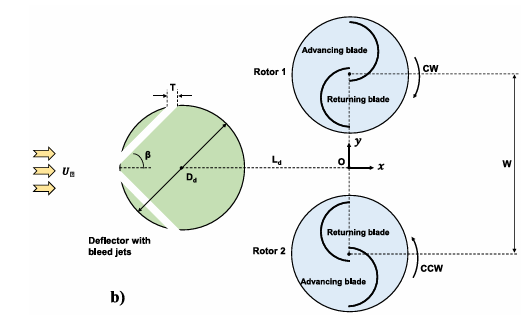
Figure 1: Schematic view of dual Savonius turbines a) details of geometry b) with deflector [1]
Simulation Process
Two traditional Savonius wind turbines are numerically examined, and the dimensions are chosen based on Roy and Saha’s experimental findings. The clockwise and counterclockwise rotations of the two rotors are in opposition to each other. Table 1 of the reference paper represents the model dimensions of the base Savonius turbine. The geometry is meticulously tailored to generate structured grid in some regions using Design Modeler software. It resulted in generation of 168823 quadrilateral + triangular cells, mostly structured quads (see Fig. 2). The circular motion of the rotor is achieved by Sliding Mesh Model. Needless to say, it requires a transient (unsteady) approach.
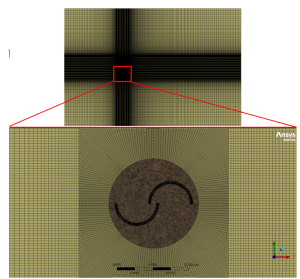
Figure 2: Hybrid mesh grid for dual Savonius turbine CFD simulation
Post-processing
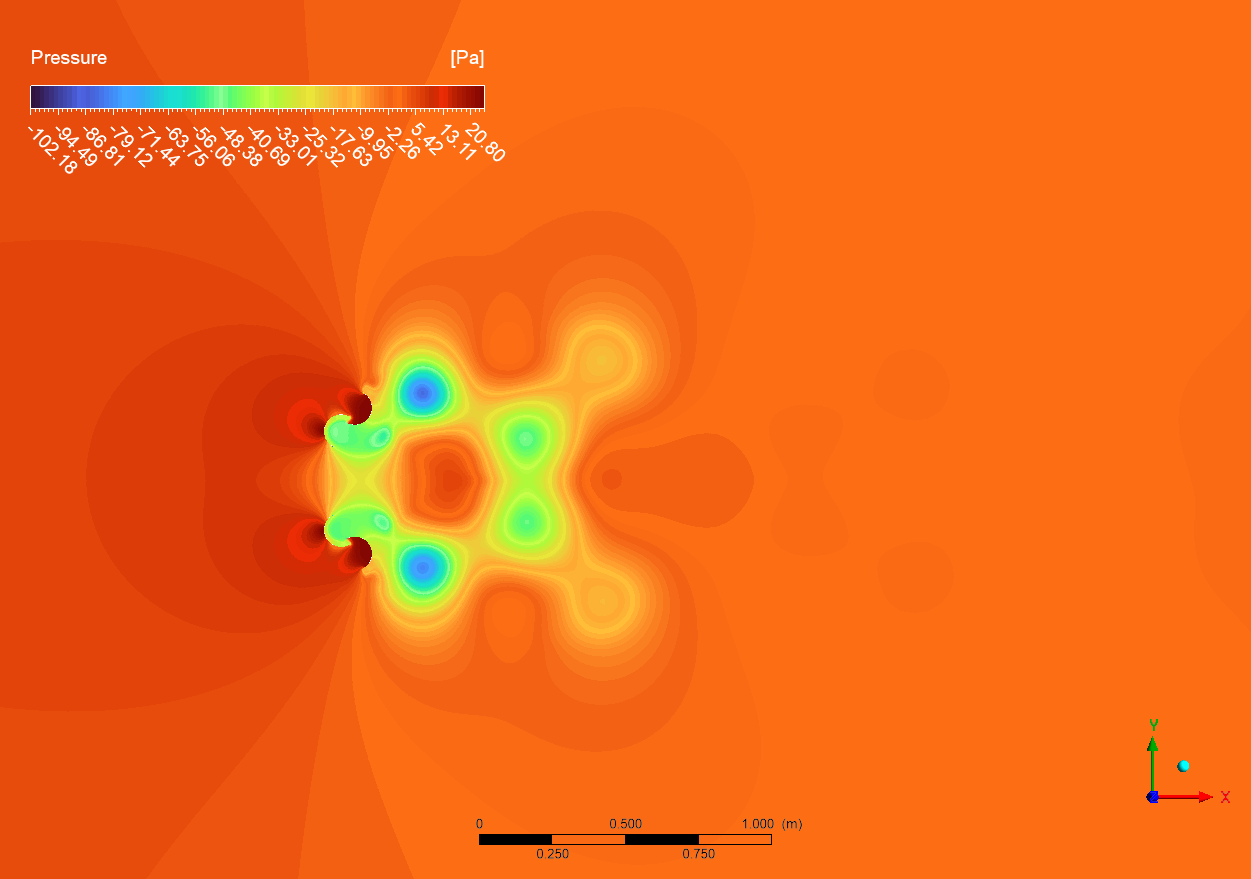
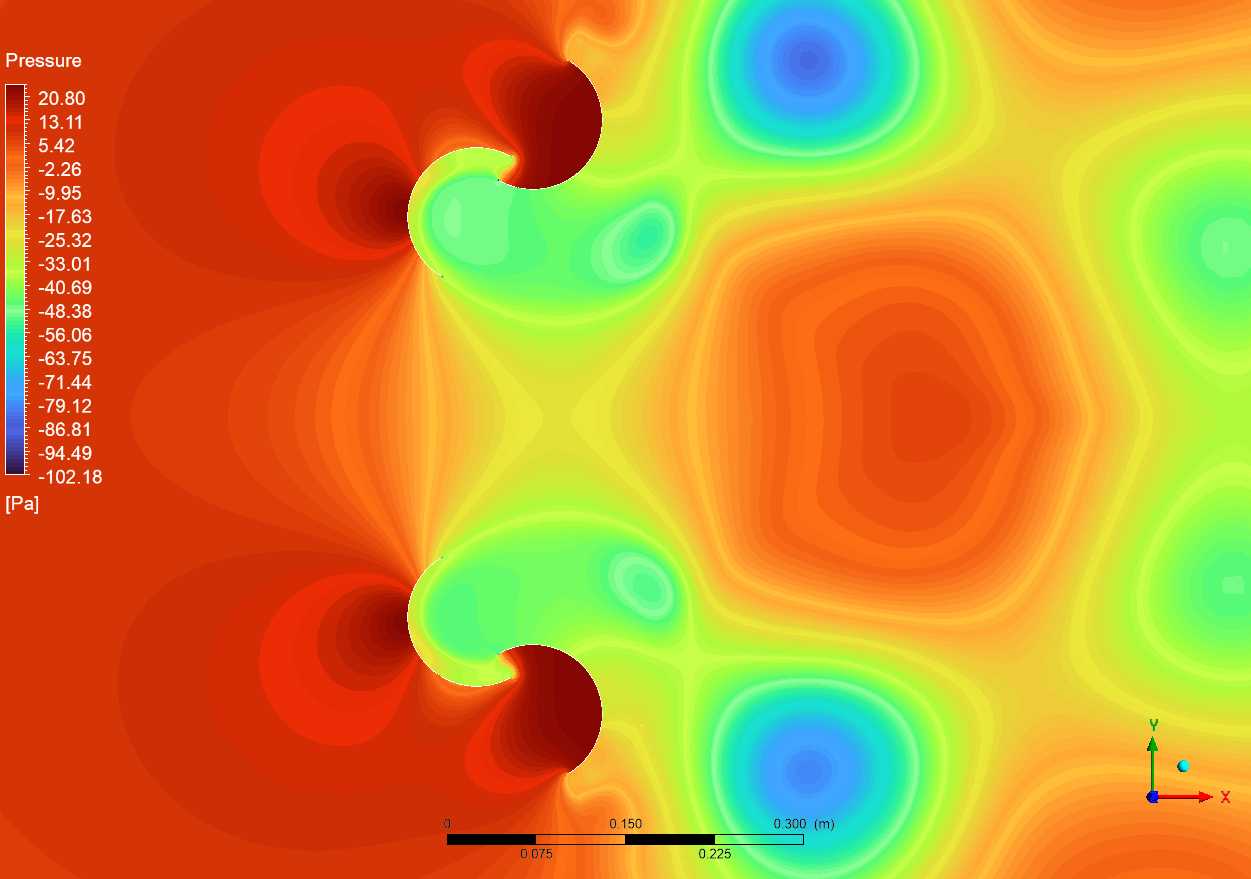
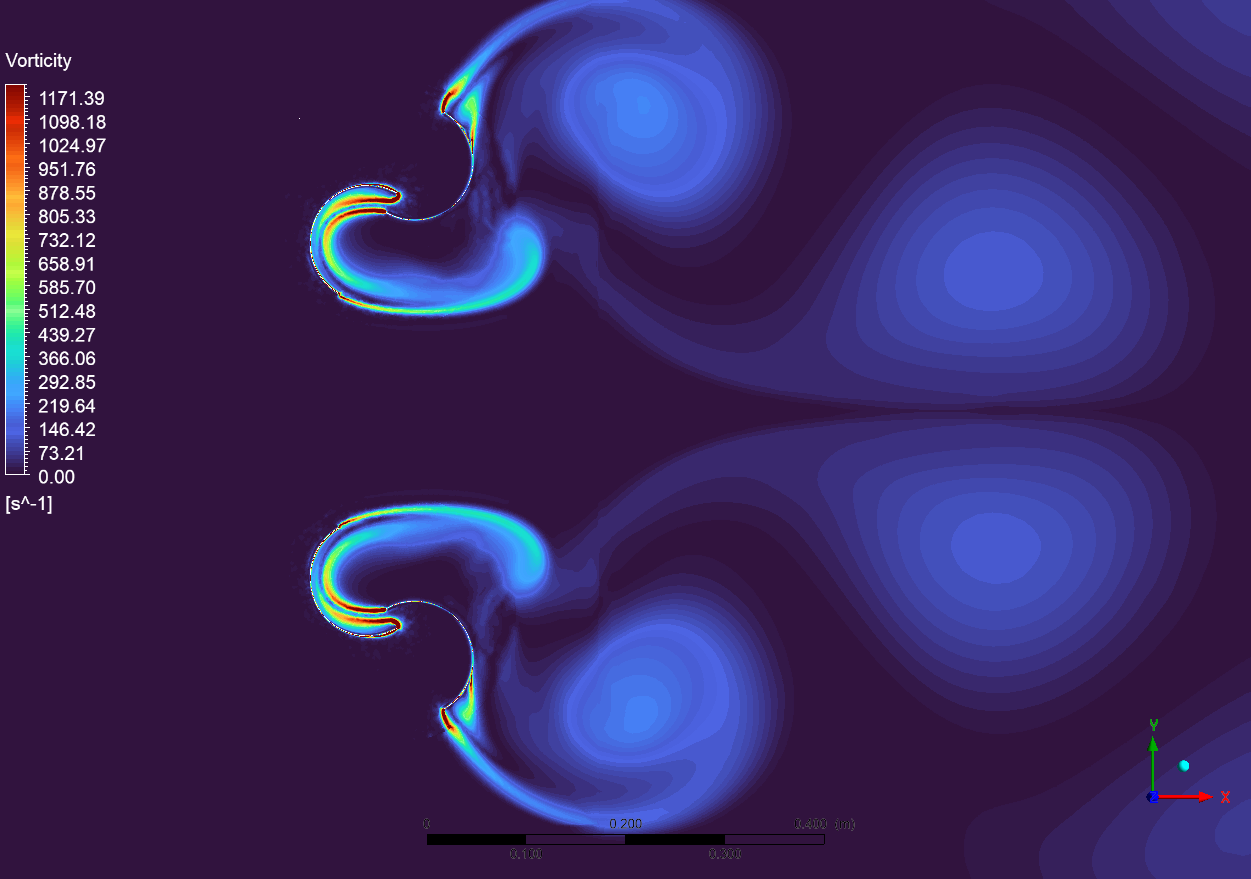
The pressure contours from the CFD simulation indicate large pressure gradients throughout the Dual Savonius turbine setup. The peak pressure of 20.80 Pa is recorded on the advancing blade surfaces (red areas), whereas the lowest pressure of -102.18 Pa is found in the concave sections of the retreating blades (dark blue areas). The significant pressure differential is essential for producing the torque required for rotation. The sliding mesh approach utilized in the simulation accurately represents the constant interaction between the stationary and revolving domains, notably noticeable in the pressure transition zones surrounding the blade surfaces. The symmetrical pressure distribution between the top and lower rotors signifies balanced loading, crucial for mechanical stability and good performance.
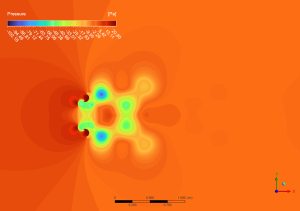
Figure 3: pressure distribution around the dual Savonius turbines
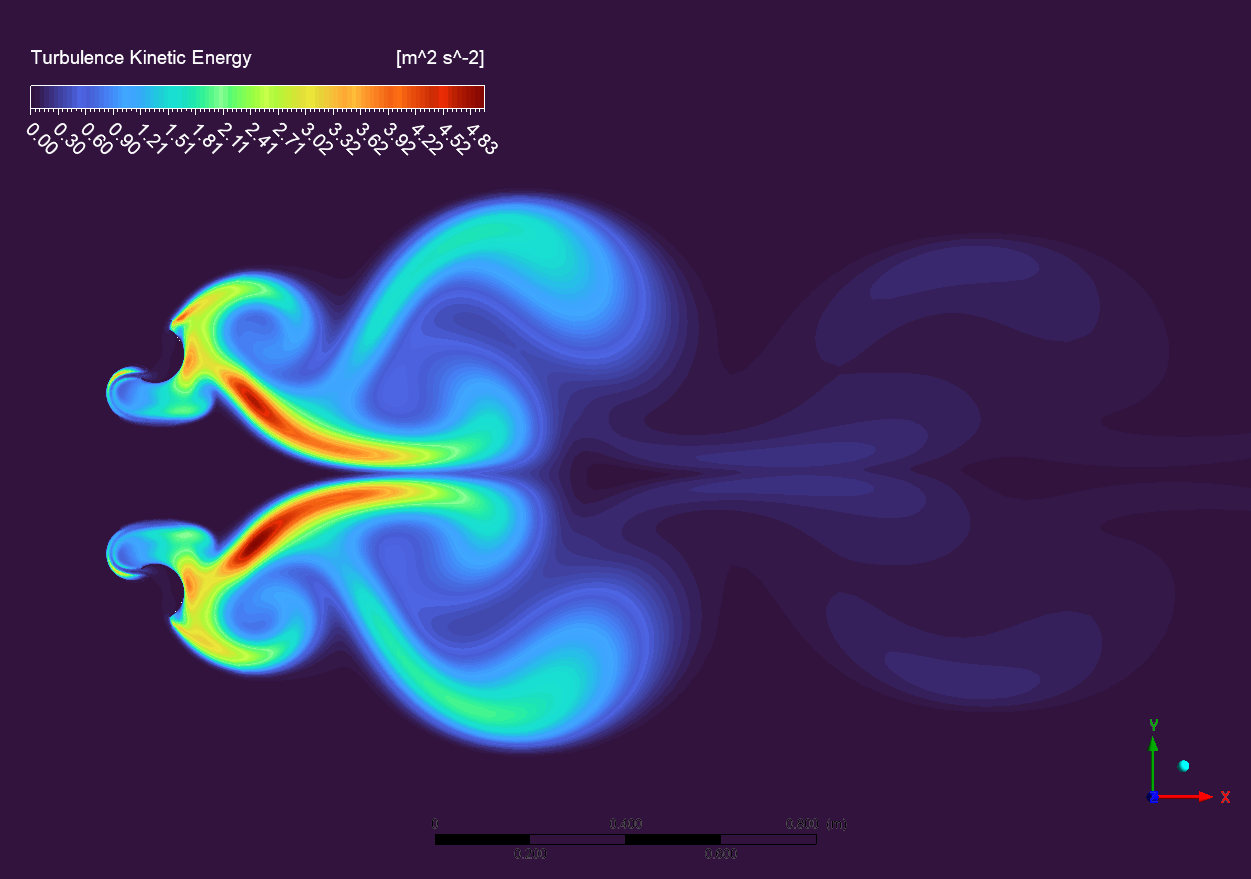
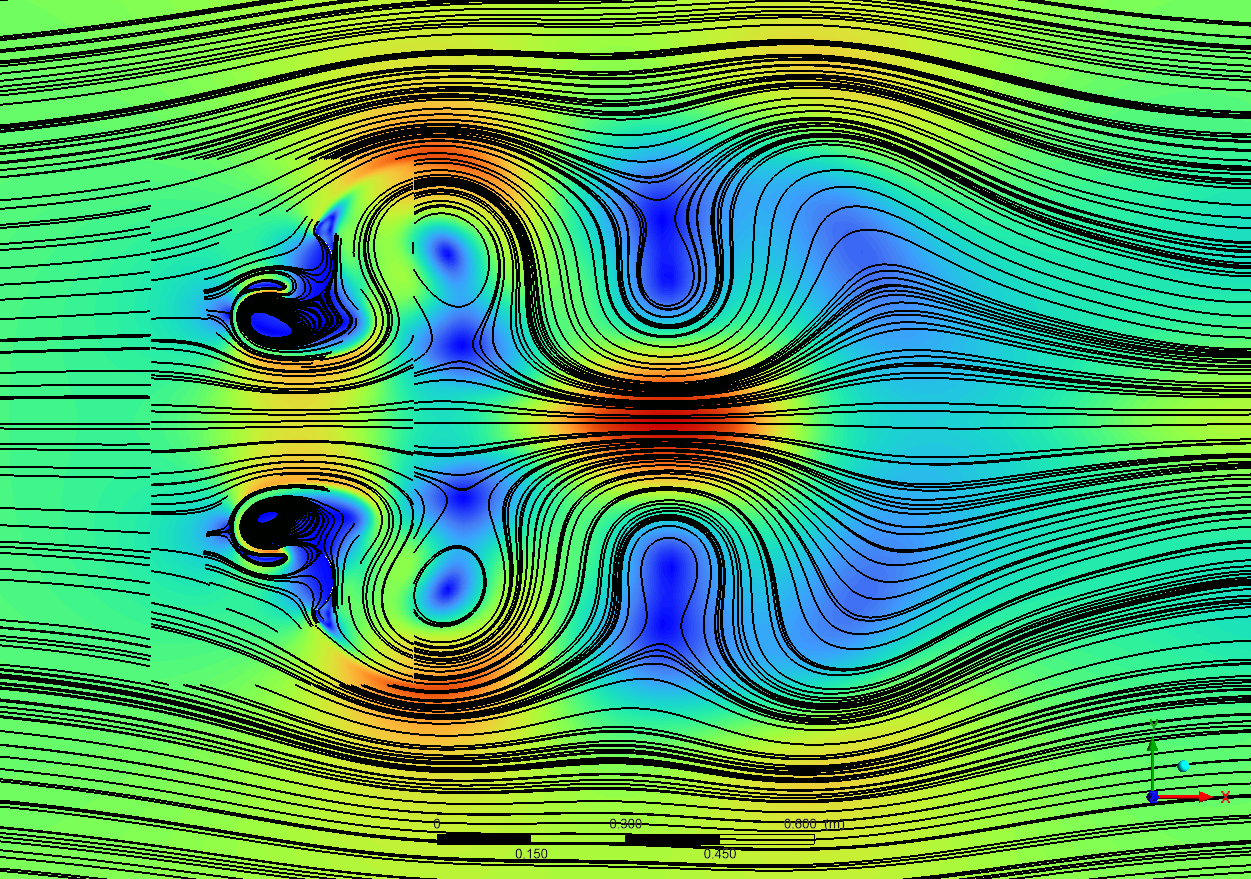
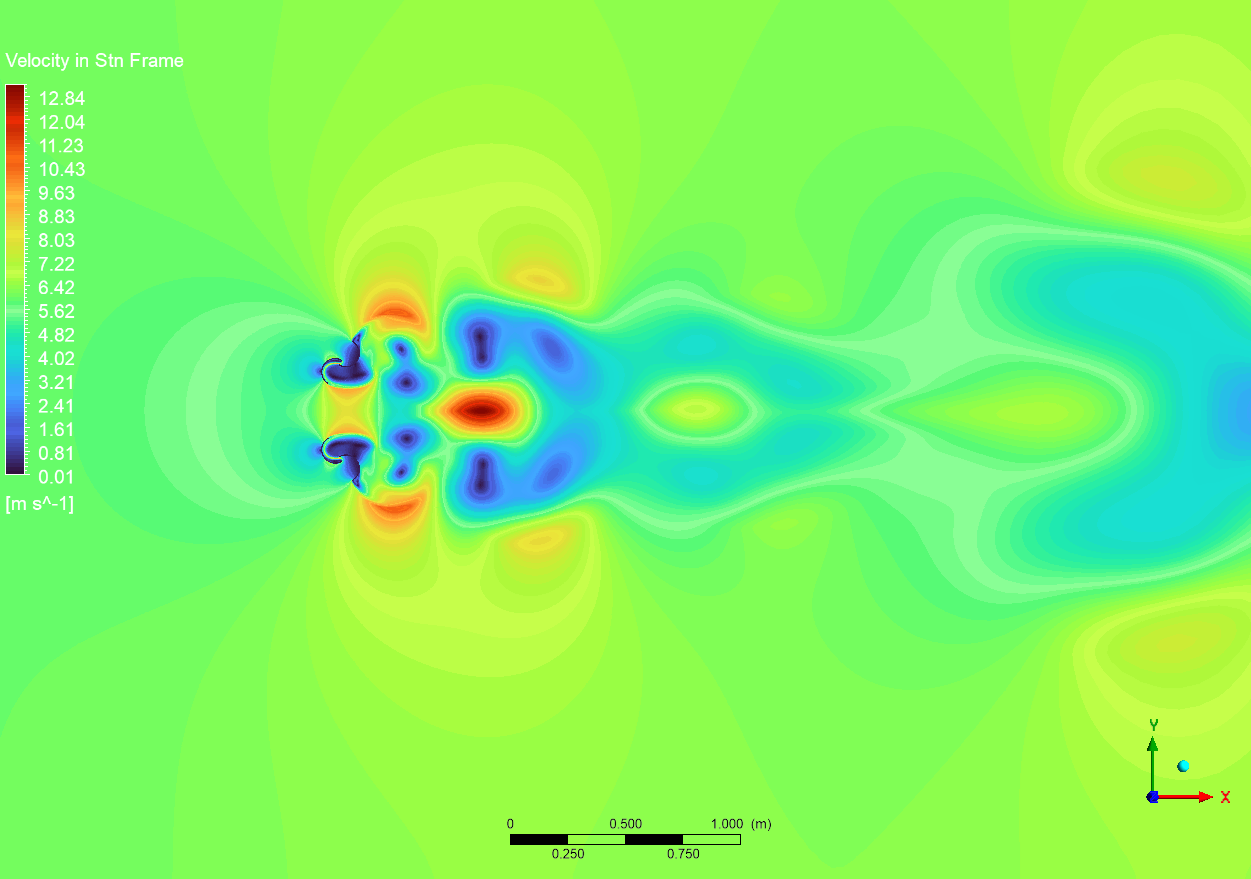
The examination of the velocity field, spanning from 0.01 to 12.84 m/s, reveals intricate flow patterns typical of Dual Savonius turbines. The velocity contours illustrate acceleration zones (red areas) adjacent to the blade tips and wake developments (blue areas) downstream of each rotor. The interaction between the two rotors is of notable engineering importance, as the wake from one rotor affects the incoming flow field of the other. The broader perspective of the velocity field illustrates the range of wake propagation, with identifiable vortex patterns observable up to 1 meter downstream. The flow characteristics obtained from the transient simulation are essential for comprehending wake interference effects and determining suitable turbine spacing in array designs. The existence of high-velocity areas (yellow to red) on the blade surfaces signifies efficient energy extraction, but the low-velocity regions (blue) in the wake represent considerable momentum transfer from the flow to the turbine system.
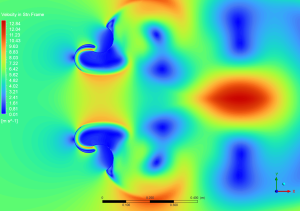
Figure 4: Velocity distribution around the dual Savonius turbines
We pride ourselves on presenting unique products at CFDLAND. We stand out for our scientific rigor and validity. Our products are not based on guesswork or theoretical assumptions like many others. Instead, most of our products are validated using experimental or numerical data from valued scientific journals. Even if direct validation isn’t possible, we build our models and assumptions on the latest research, typically using reference articles to approximate reality.
Yes, we’ll be here . If you have trouble loading files, having technical problems, or have any questions about how to use our products, our technical support team is here to help.
You can load geometry and mesh files, as well as case and data files, using any version of ANSYS Fluent.
€220.00 Original price was: €220.00.€195.00Current price is: €195.00.

€325.00 Original price was: €325.00.€195.00Current price is: €195.00.

€185.00 Original price was: €185.00.€135.00Current price is: €135.00.

€165.00 Original price was: €165.00.€125.00Current price is: €125.00.

€245.00 Original price was: €245.00.€185.00Current price is: €185.00.

€240.00 Original price was: €240.00.€135.00Current price is: €135.00.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.