Erosion In A Bent Pipe CFD Simulation Using DPM | ANSYS Fluent Tutorial
Erosion In A Bent Pipe CFD Simulation Using DPM | ANSYS Fluent Tutorial
- Upon ordering this product, you will be provided with a geometry file, a mesh file, and an in-depth Training Video that offers a step-by-step training on the simulation process.
- For any more inquiries regarding the product, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at info@CFDLAND.com or through our online support assistant.
€0.00
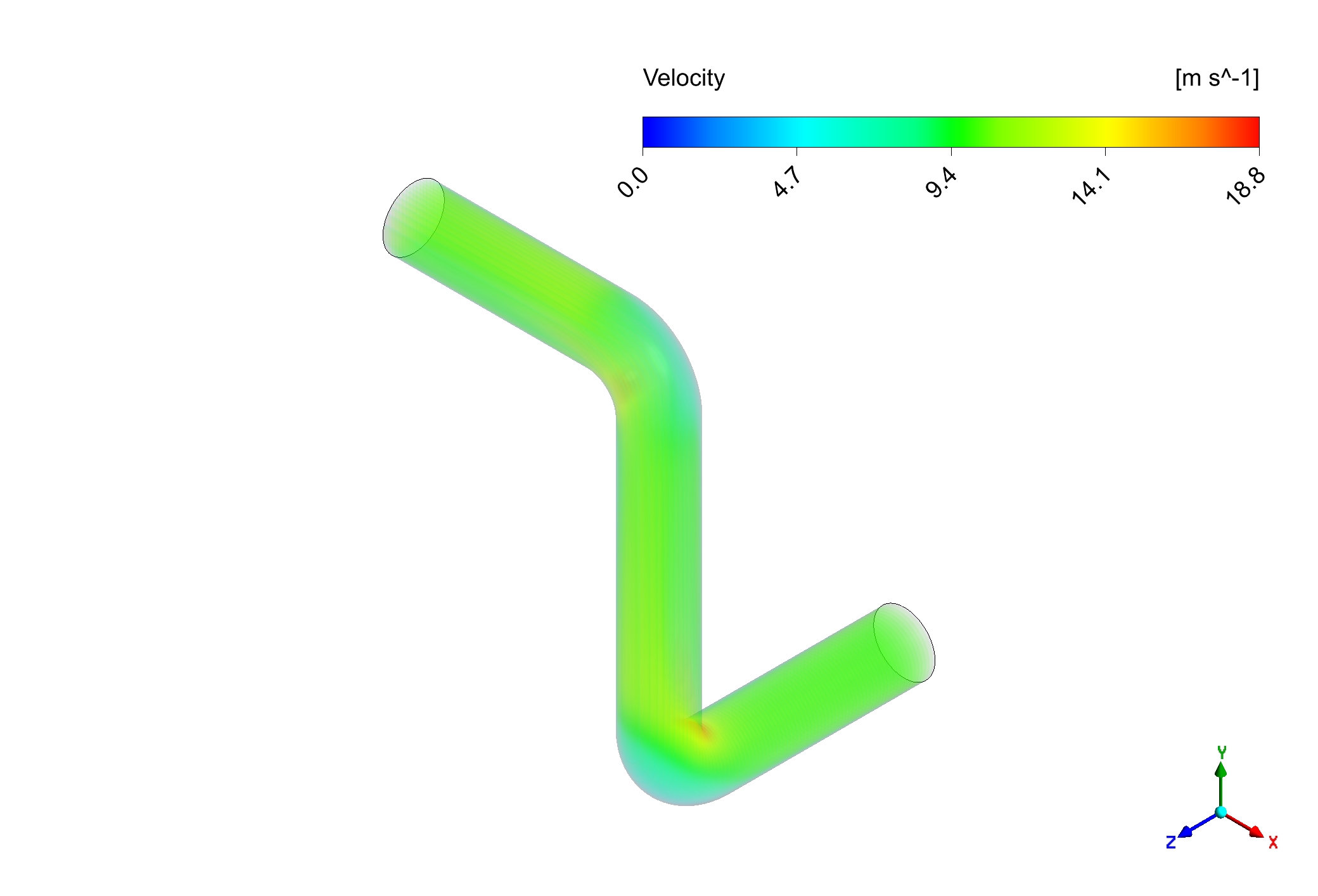
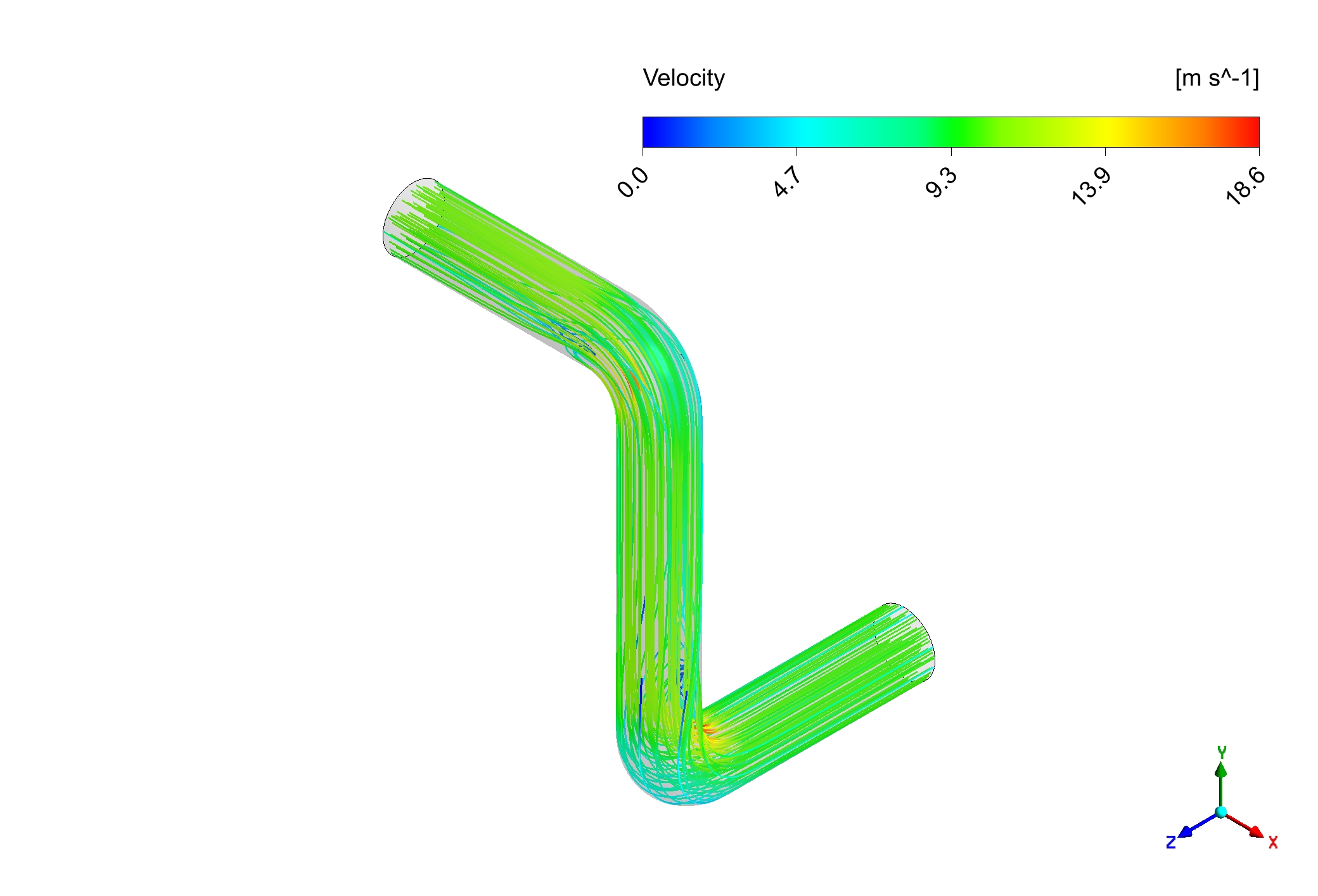
Like an unseen opponent, erosion persistently targets the interior of pipes in a variety of industries, including water treatment, oil and gas, and even your home plumbing. If ignored, this ongoing wear and tear can result in expensive repairs, unplanned shutdowns, and even catastrophes. Maintaining safe and effective operations requires an understanding of where and how erosion occurs. The issue is particularly serious around pipe elbows and bends, where the movement of gases and liquids can cause severe damage. This free lesson takes on this problem head-on by showing you how to use the potent simulation program ANSYS Fluent to forecast and stop erosion. Come along as we delve into the realm of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and provide you with the knowledge and skills necessary to protect your piping systems from this imperceptible yet deadly force. In this enthralling study, Discrete Phase Model (DPM) is utilized.
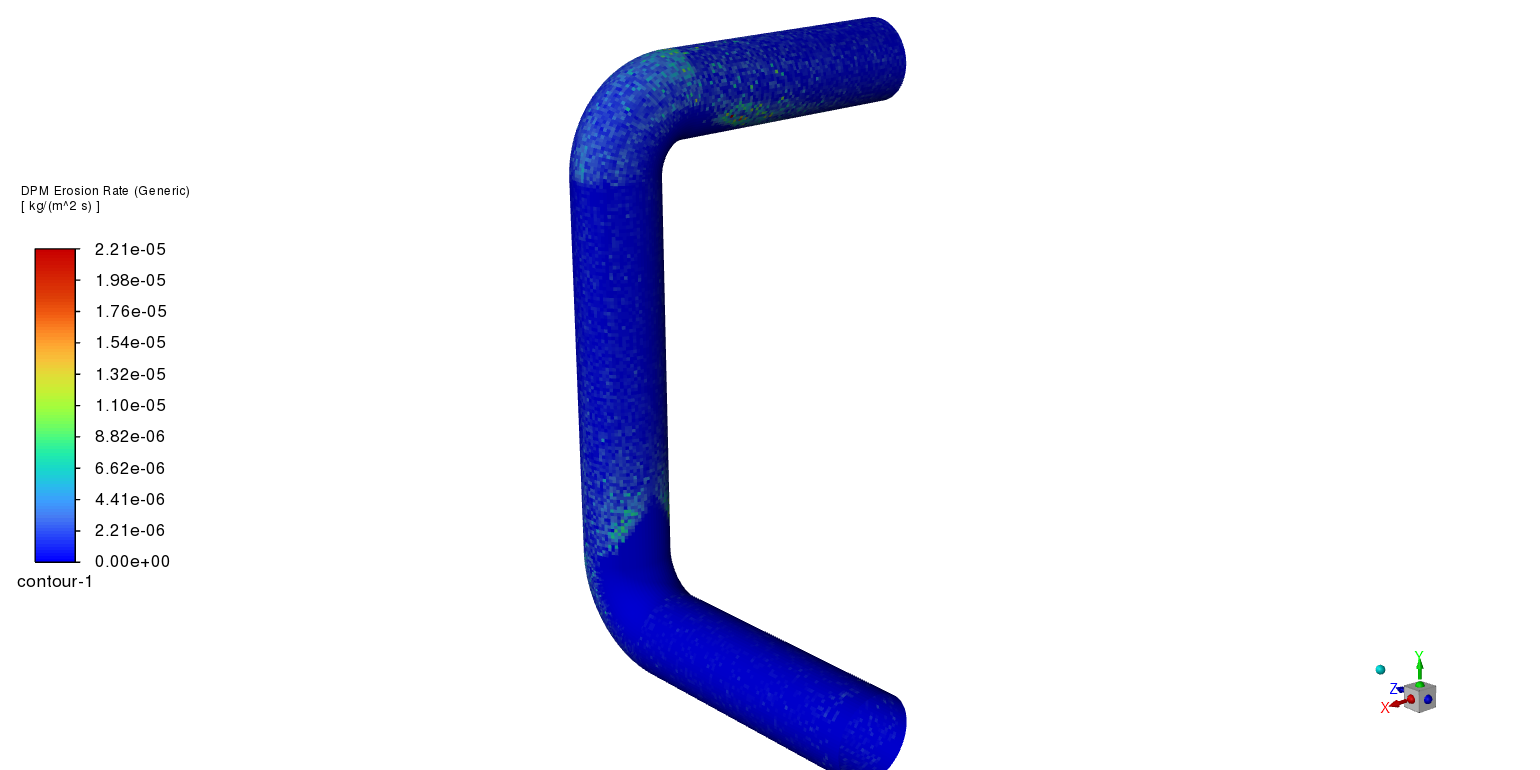
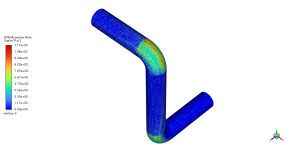
Figure 1: Erosion inside a bent pipe CFD Simulation Using DPM
Simulation Process
The geometry model which is a bent pipe is erected using Design Modeler software. It transferred into ANSYS Meshing for production of high-qualified Hexagonal elements but not structured. 5 boundary layers are established to precisely predict the flow behavior near wall`s regions. The solver settings are all set. Erosion/Accretion investigation requires the activation of Discrete Phase Model (DPM) module which tracks the dispersed phase in Lagrangian Framework. In other words, this is a multiphase study including water as continuous phase and sands as discrete phase. Among provided erosion models by ANSYS Fluent, Generic is opted. Think of it as a simplified or adaptable framework that can be applied across various materials and conditions, especially when you don’t have detailed, material-specific data. It uses more universal parameters and equations to give you a broader estimate of erosion rates.
Figure 2: Hexagonal cells spread over Bent pipe
Post-processing
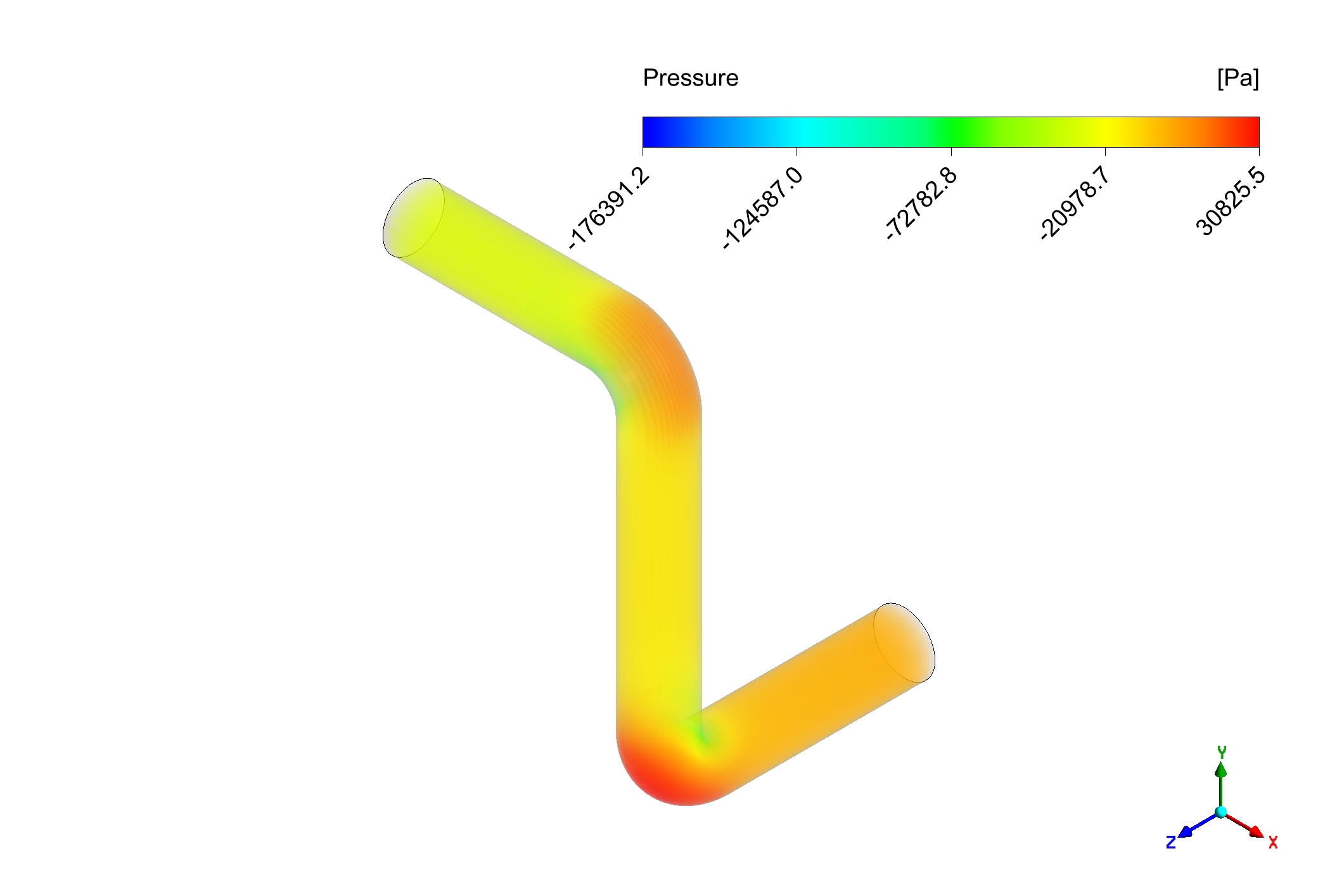
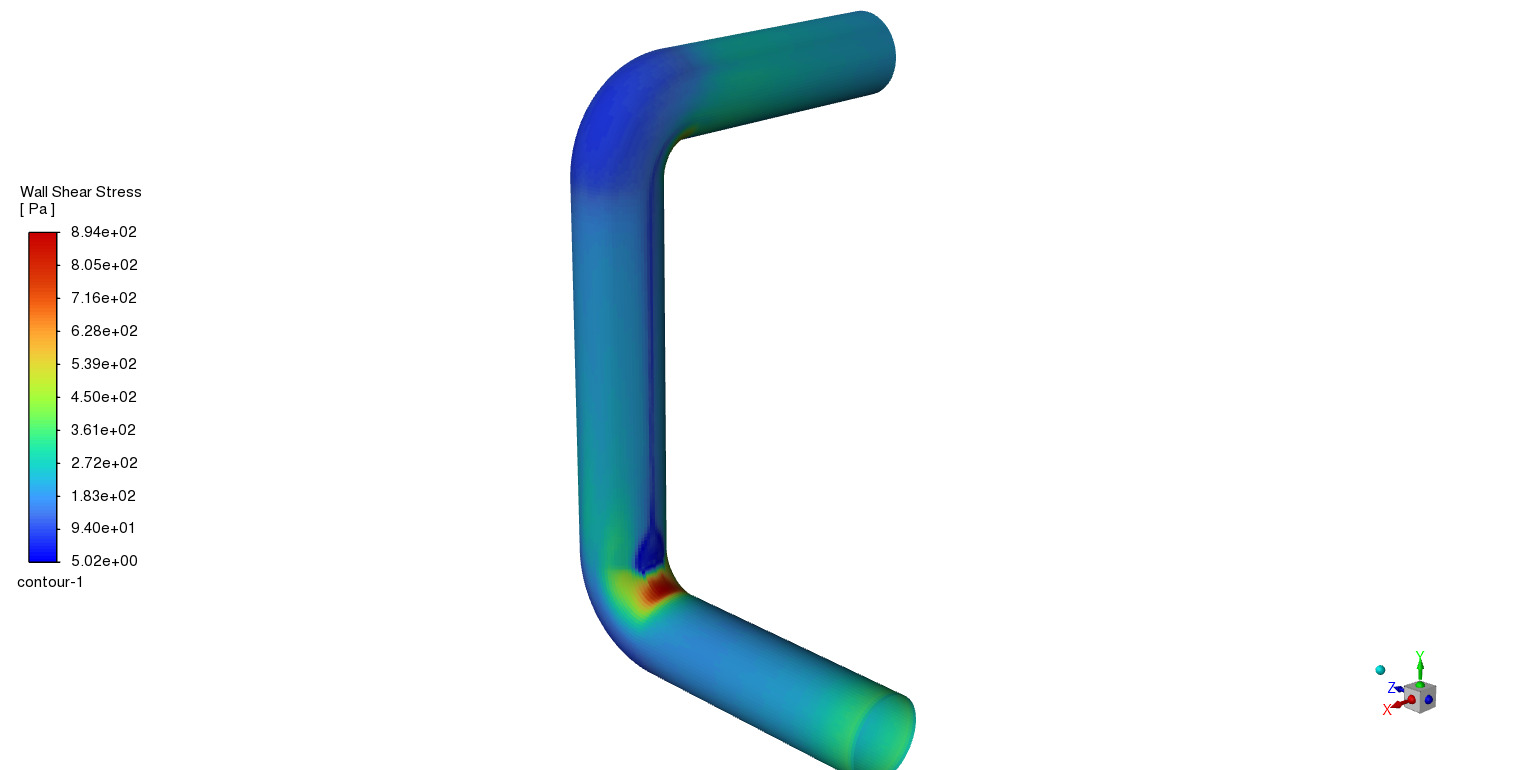
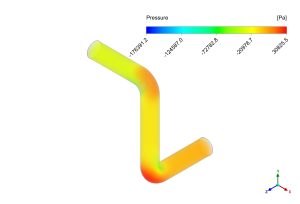
The CFD simulation demonstrates a distinct pattern of increased wall shear stress that is concentrated at the outer radius of the elbow and peaks at about 894 Pascals. The fluid’s forced direction change at the bend is the direct cause of this localized stress concentration. A zone of high velocity and, as a result, high shear is created when the fluid impinges on the outer wall due to its inertia. This phenomena is in alignment with basic fluid mechanics concepts, which state that flow curvature contributes to the uneven distribution of shear stress by causing pressure gradients and secondary flows. A less significant flow interaction in this zone is shown by the comparatively lower shear stress throughout the inner radius.
Figure 3) a) shear stress b) pressure gradient inside the elbow
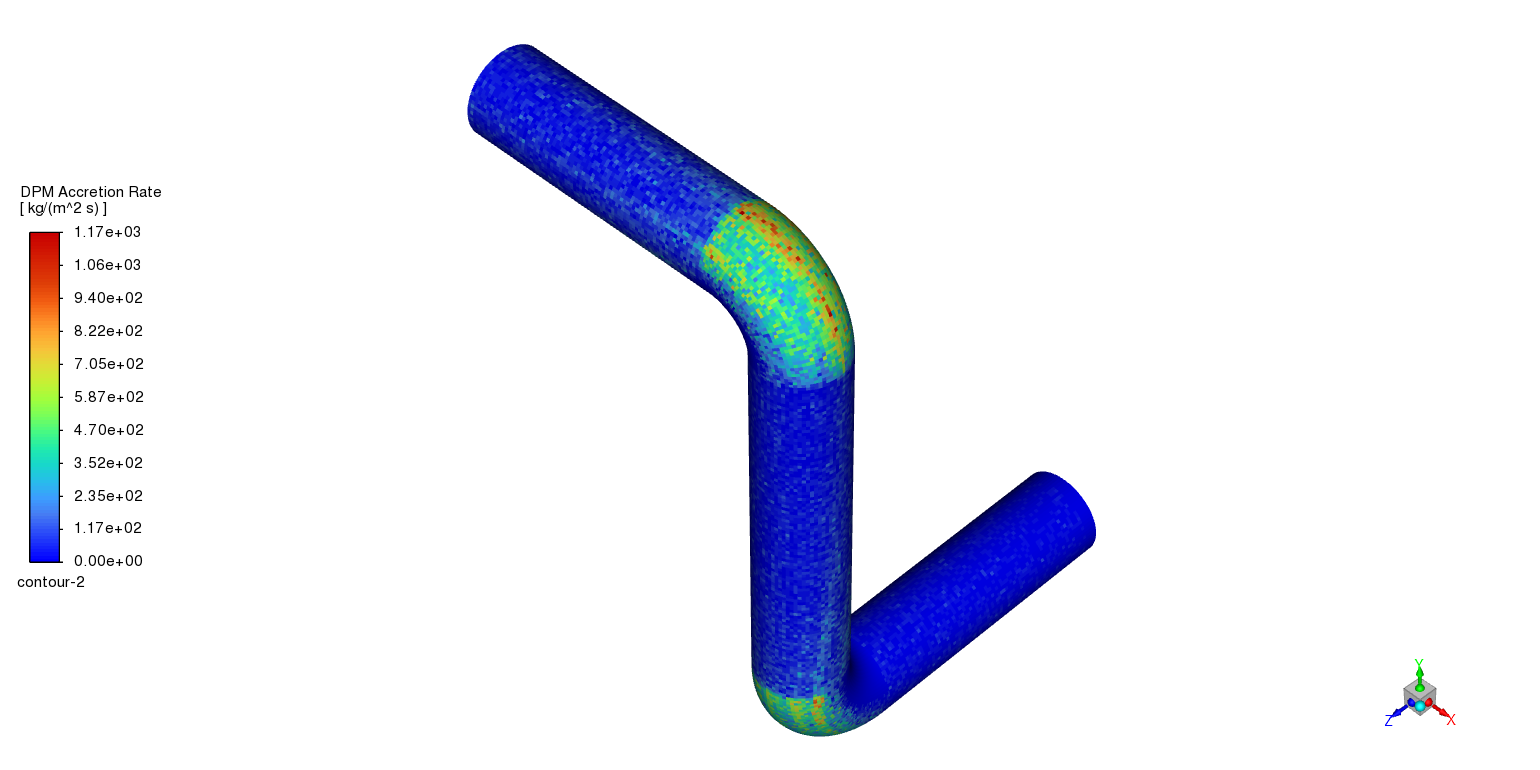
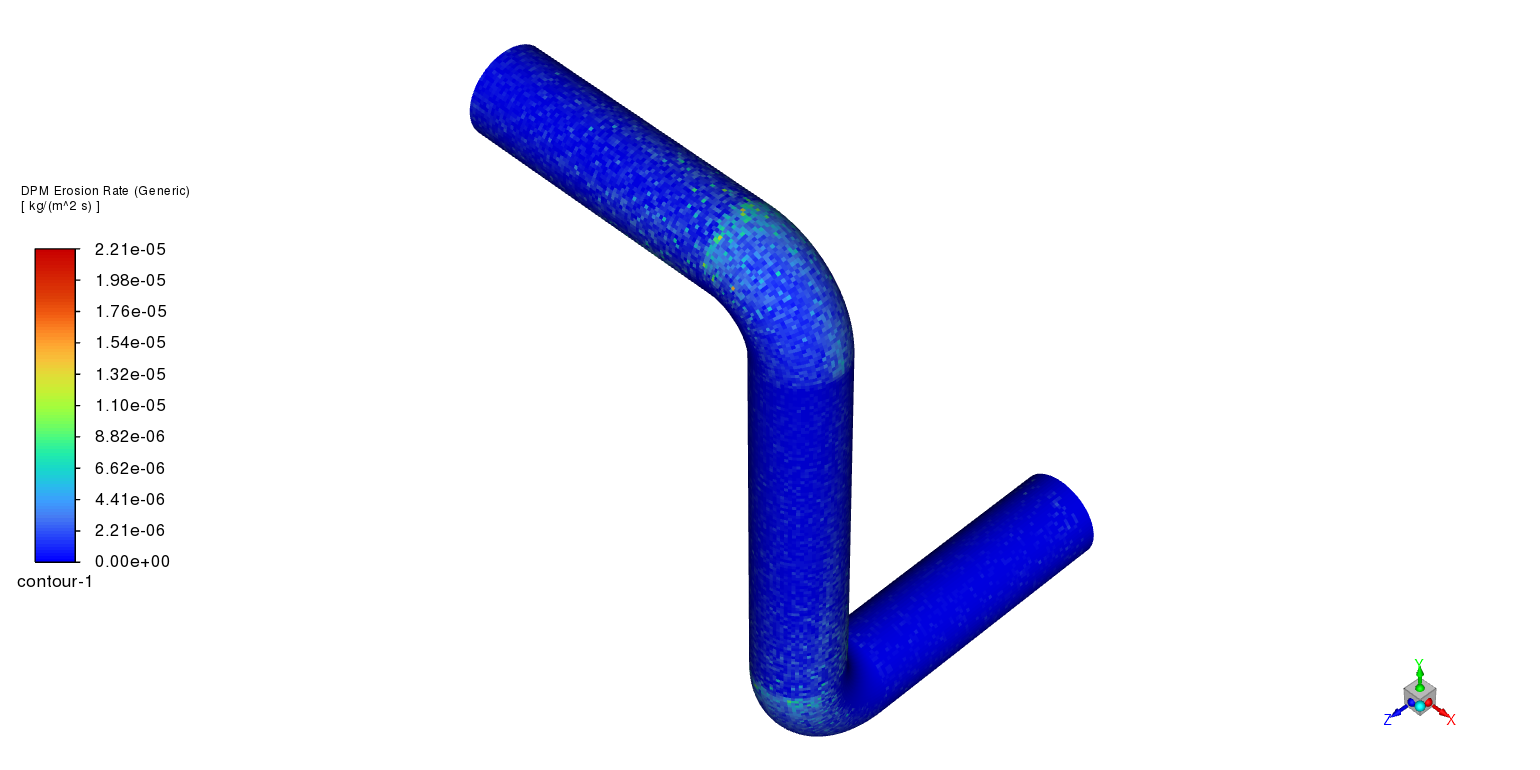
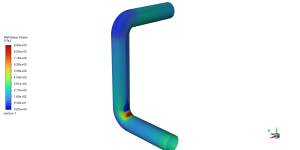
An elbow pipe’s accretion and erosion patterns were examined using CFD, which showed a crucial interaction between corrosion of the material and flow dynamics. According to the analysis, the fluid’s change in direction and increased momentum create particle impingement, which results in the highest erosion rates in the outer bend. On the other hand, accretion is visible in the inner bend, where destroyed material builds up in the lower velocity zone. Because of the substantial effects these localized events have on pipe integrity and system performance, design and maintenance procedures must take erosion and accretion into account. The results highlight the usefulness of CFD models in anticipating these impacts and directing preventative actions, including material choice, geometric adjustments, and routine cleaning, to guarantee the long-term dependability and performance of piping systems.
Figure 4: Accretion/Erosion inside the elbow by Generic Model
We pride ourselves on presenting unique products at CFDLAND. We stand out for our scientific rigor and validity. Our products are not based on guesswork or theoretical assumptions like many others. Instead, most of our products are validated using experimental or numerical data from valued scientific journals. Even if direct validation isn’t possible, we build our models and assumptions on the latest research, typically using reference articles to approximate reality.
Yes, we’ll be here . If you have trouble loading files, having technical problems, or have any questions about how to use our products, our technical support team is here to help.
You can load geometry and mesh files, as well as case and data files, using any version of ANSYS Fluent.
€230.00 Original price was: €230.00.€185.00Current price is: €185.00.

€185.00 Original price was: €185.00.€155.00Current price is: €155.00.

€260.00 Original price was: €260.00.€135.00Current price is: €135.00.

€240.00 Original price was: €240.00.€125.00Current price is: €125.00.

€210.00 Original price was: €210.00.€155.00Current price is: €155.00.

















1 review for Erosion In A Bent Pipe CFD Simulation Using DPM | ANSYS Fluent Tutorial
Daniel Sami (verified owner) –
Looks like a nice TUTORIAL