CO2 Methanation CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Training
CO2 Methanation CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Training
- Upon ordering this product, you will be provided with a geometry file, a mesh file, and an in-depth Training Video that offers a step-by-step training on the simulation process.
- For any more inquiries regarding the product, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at info@CFDLAND.com or through our online support assistant.
€165 Original price was: €165.€105Current price is: €105.
The process of CO2 methanation, commonly called the Sabatier reaction, involves the breakdown of carbon dioxide and hydrogen into methane and water, facilitated by a metal catalyst, usually nickel. This reaction is essential in strategies for gathering and utilizing carbon through the transformation of greenhouse gases into valuable synthetic natural gas, which can be easily incorporated into present facilities. The exothermic characteristics of the reaction render it especially appealing for energy storage applications, particularly when integrated with renewable energy sources. Through the recycling of CO2 and the storage of surplus renewable energy, CO2 methanation plays a crucial role in advancing a sustainable and circular energy economy, enhancing energy security and aiding in the reduction of carbon emissions. In the current CFD study, CO2 methanation is simulated based on reference papers and theses.
Co2+ H2 ===> 2H2O + 1CH4

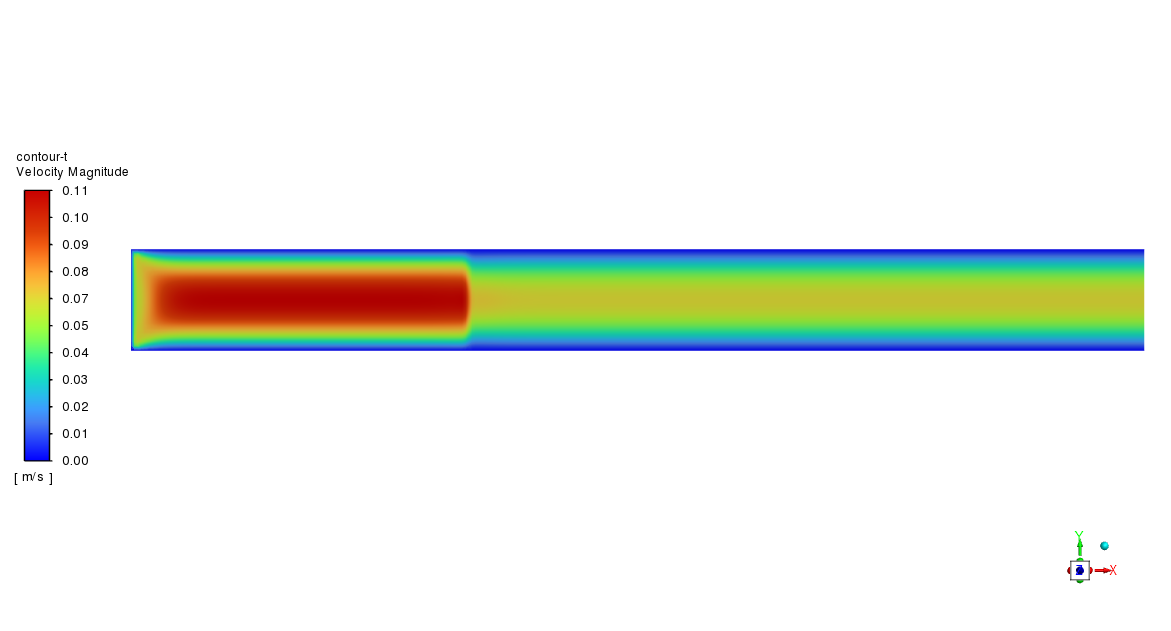
Figure 1: Outline of CO2 Methanation CFD Simulation
Simulation Process
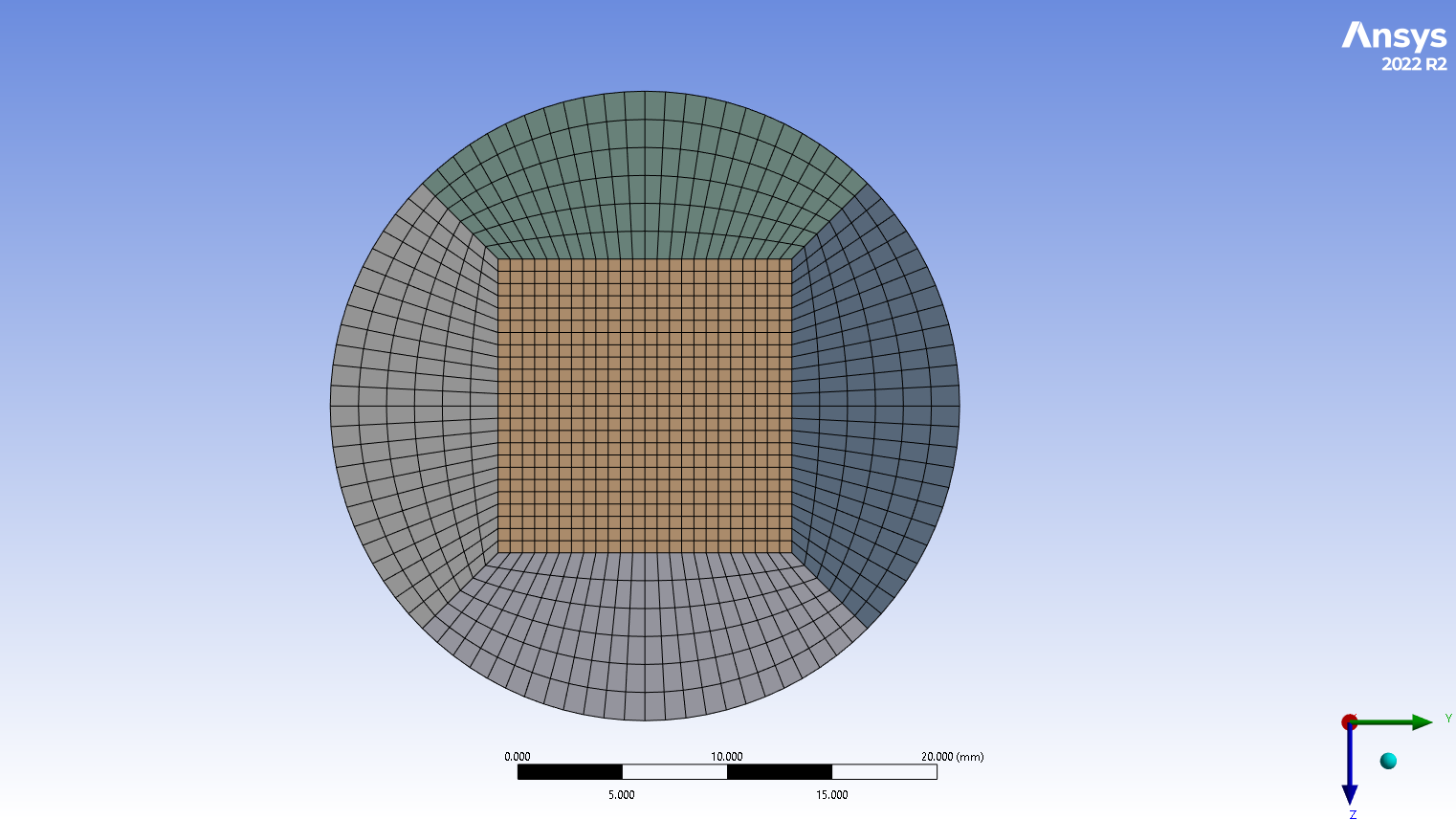
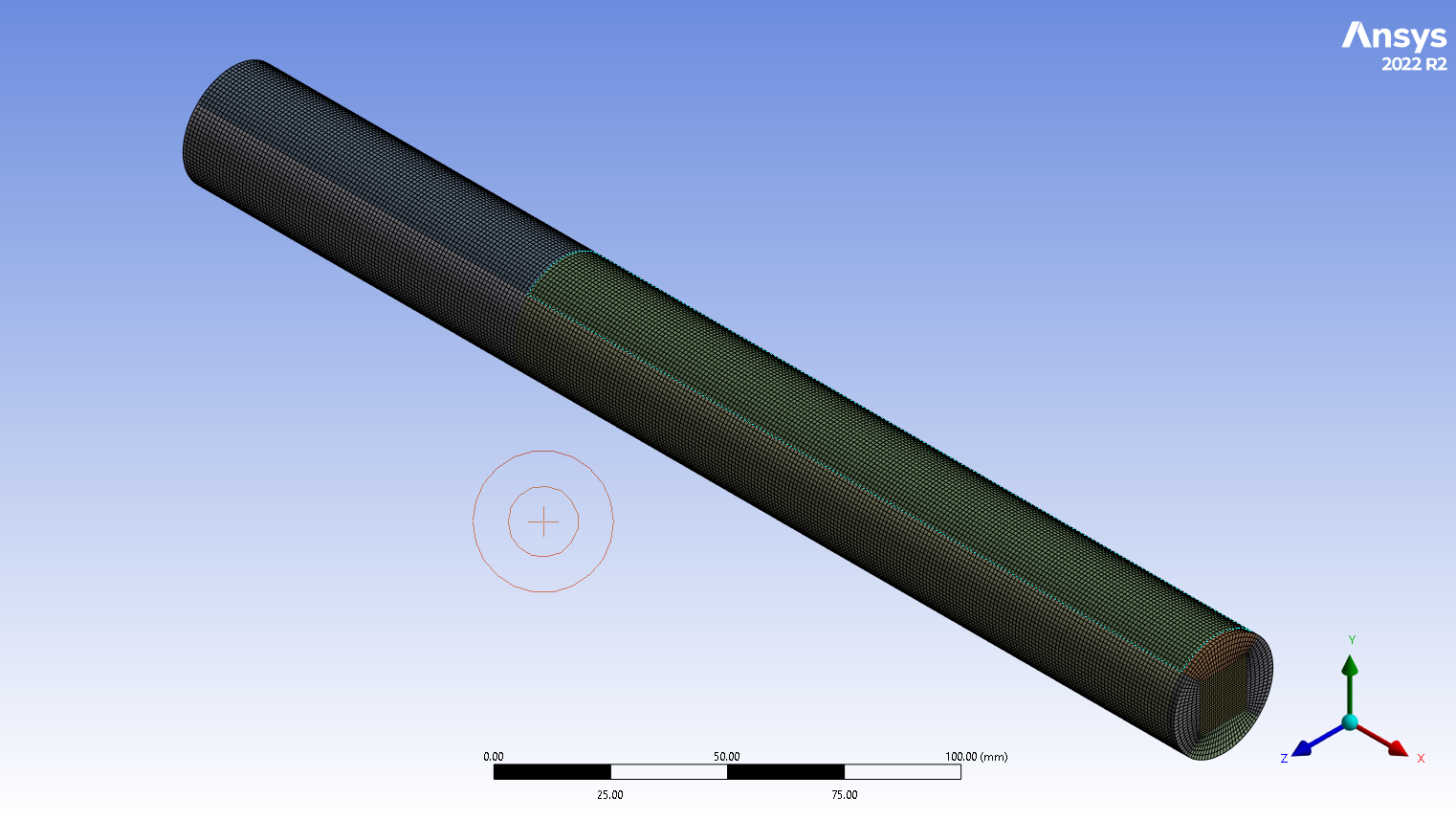
The cylindrical reactor chamber was initially designed using Design Modeler software, considering proper blocking that will help during the meshing process. 345600 hexagonal elements establish the domain, resulting in a high-quality structured grid. The volumetric reactions require activation on the Species Transport module, followed by the Finite-Rate/No TCI model. The mixture properties are mostly a function of temperature. Thus, a User-defined Function is written to adopt specific heat, Plus a Polynomial sub-model for other properties such as thermal conductivity and viscosity. More importantly, as shown in Fig.1, the reactions must occur in the reactor’s middle section. This is another essential assumption that the simulation needed.
Figure 2: Structured grid generated over CO2 Methanation CFD Simulation
Post-processing
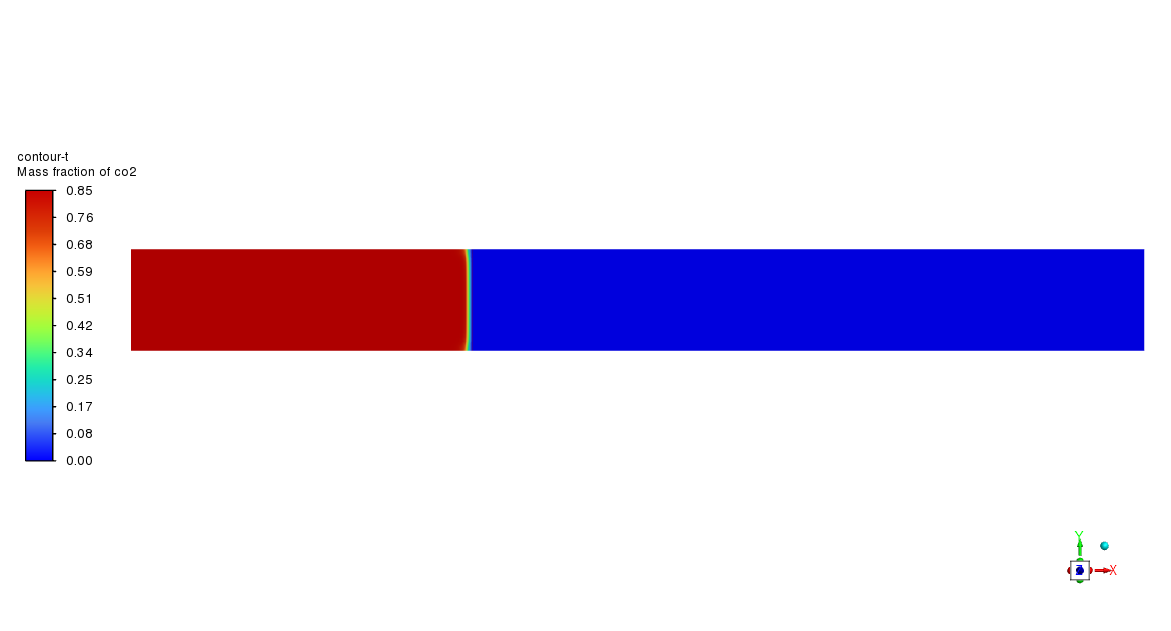
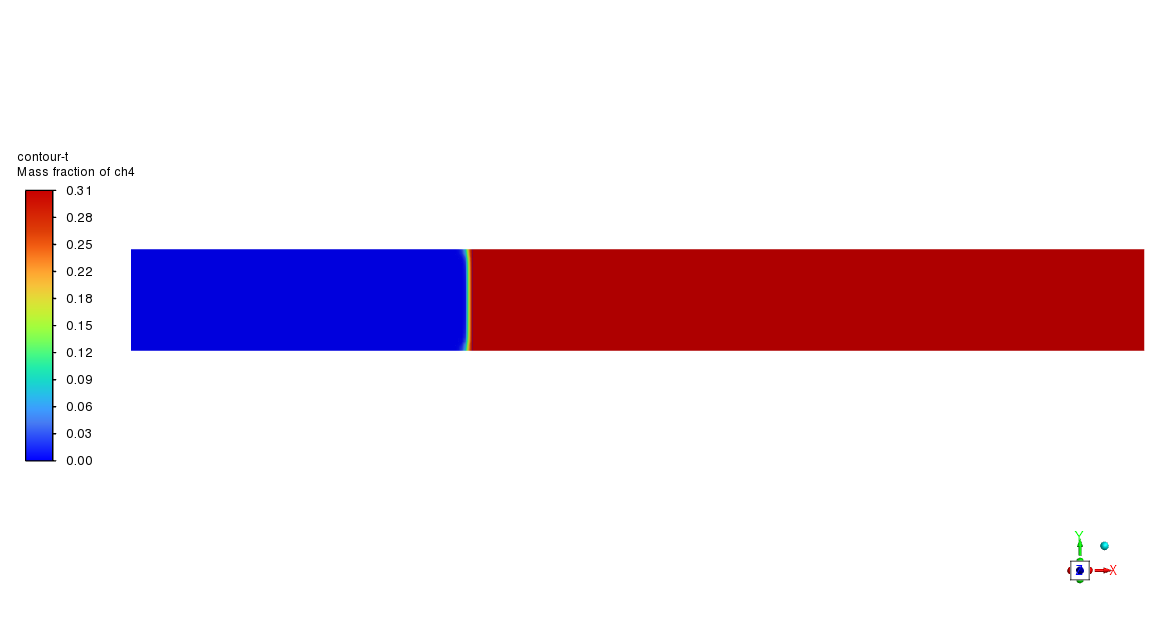
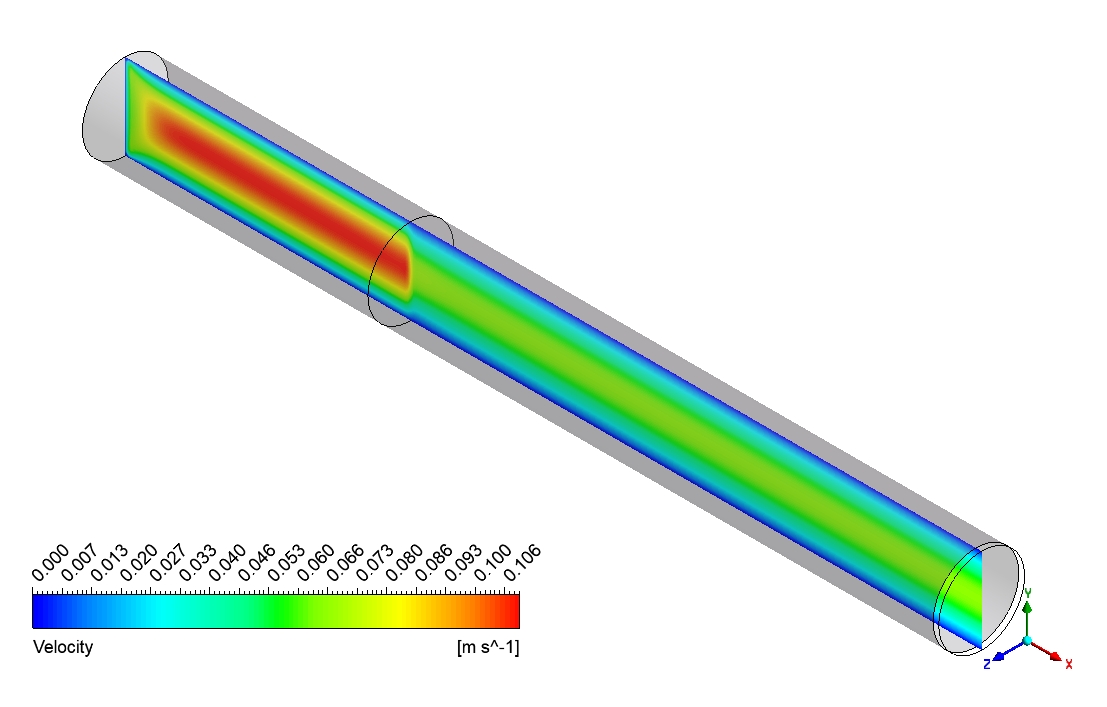
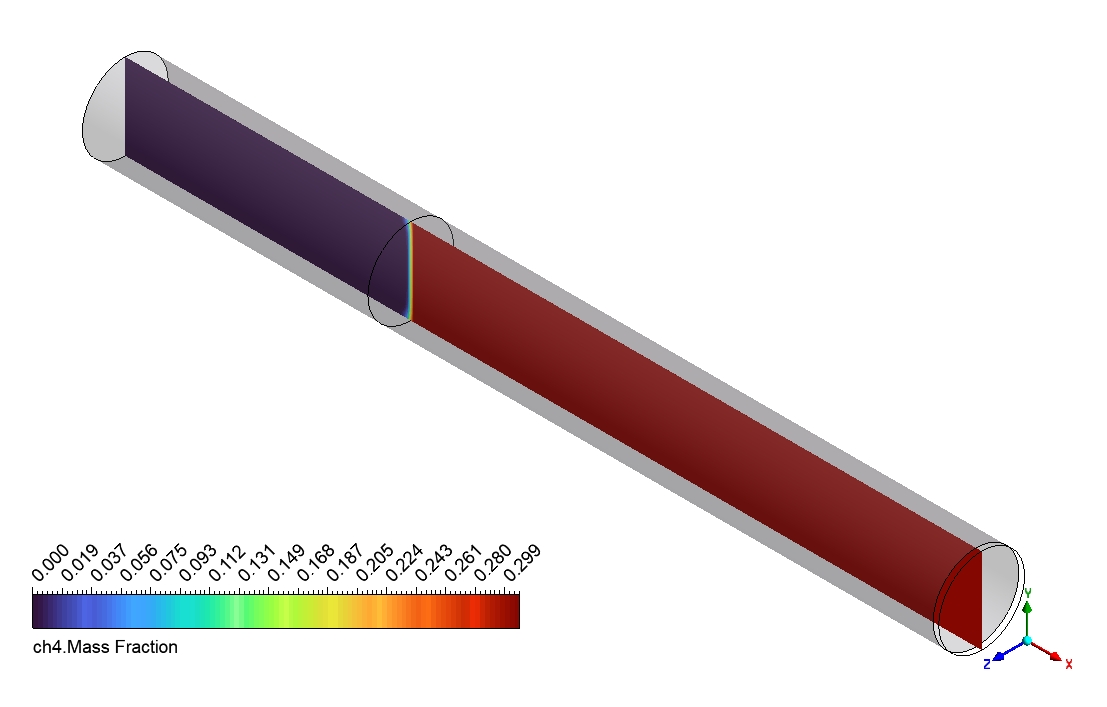
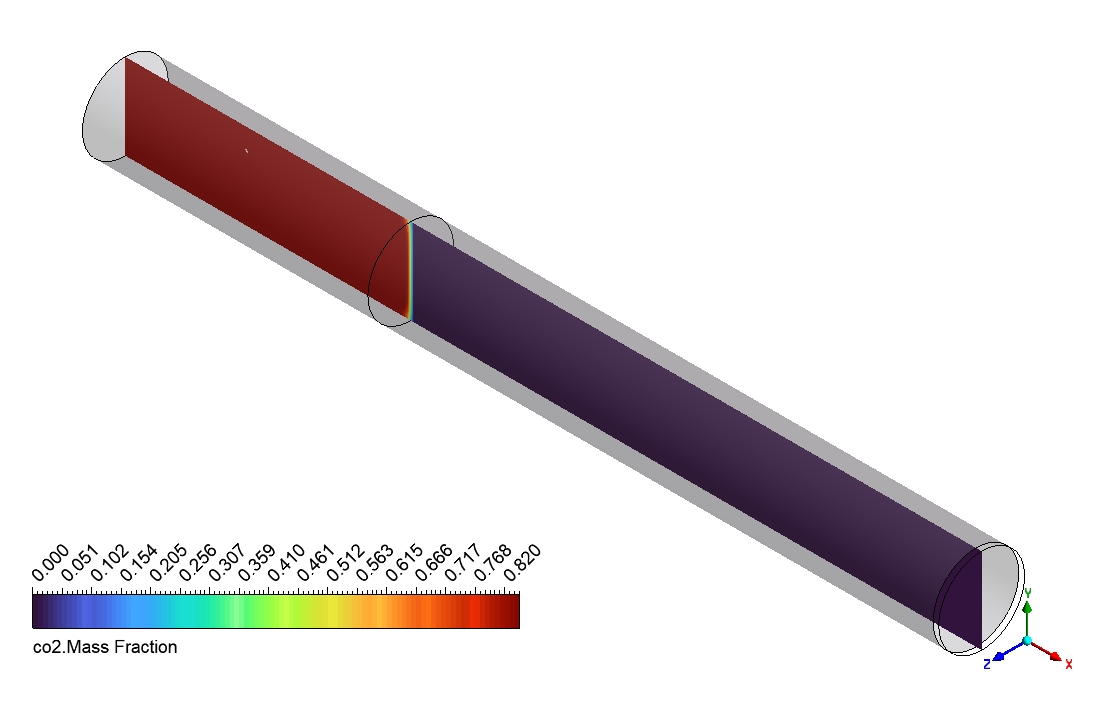
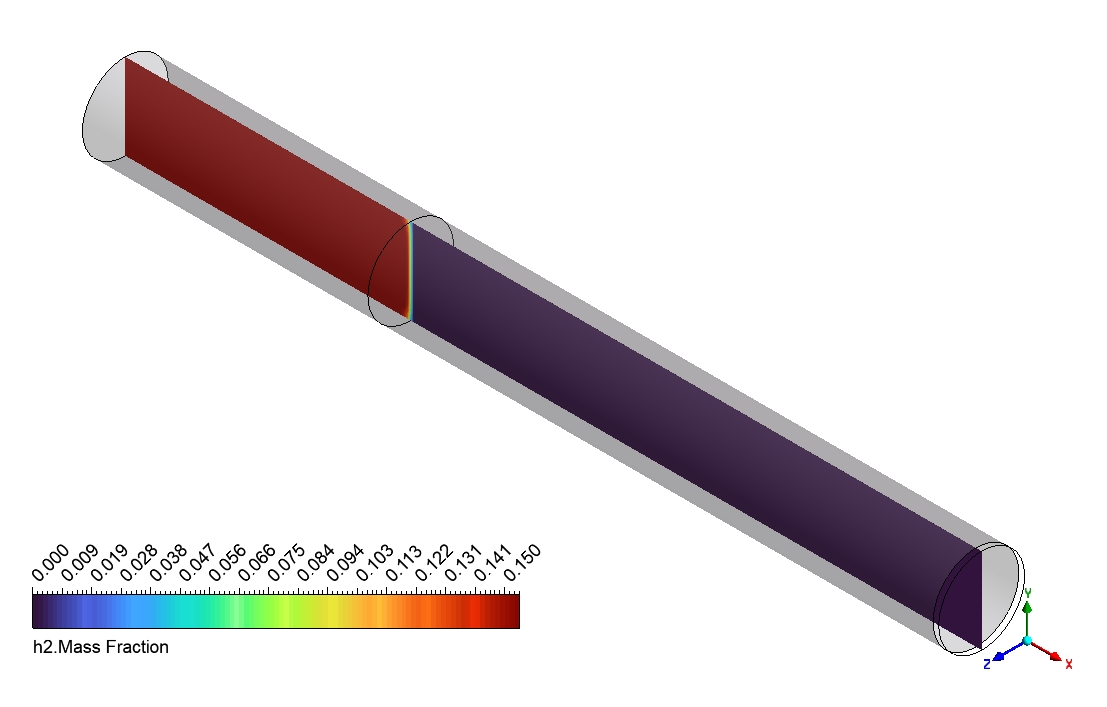
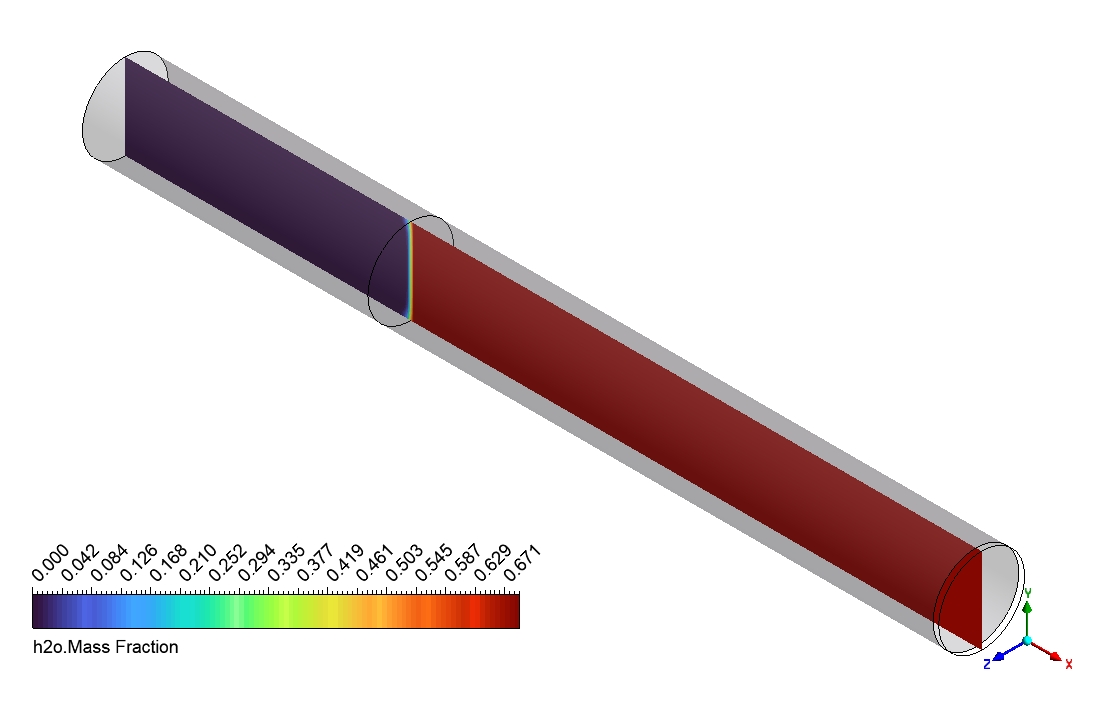
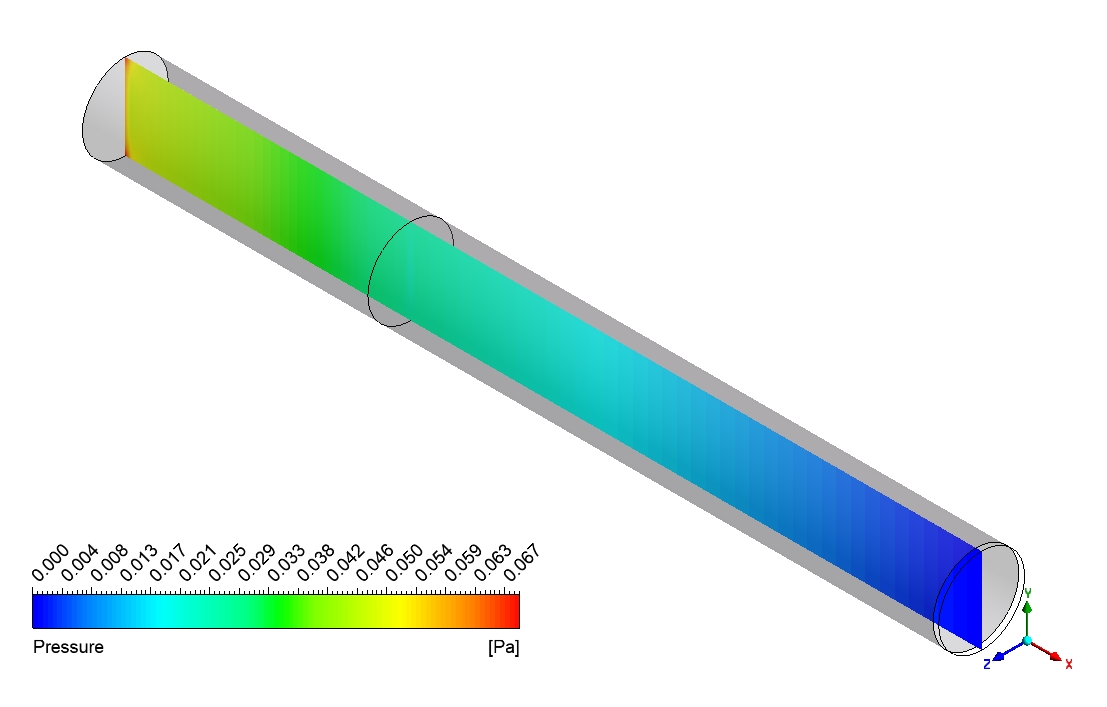
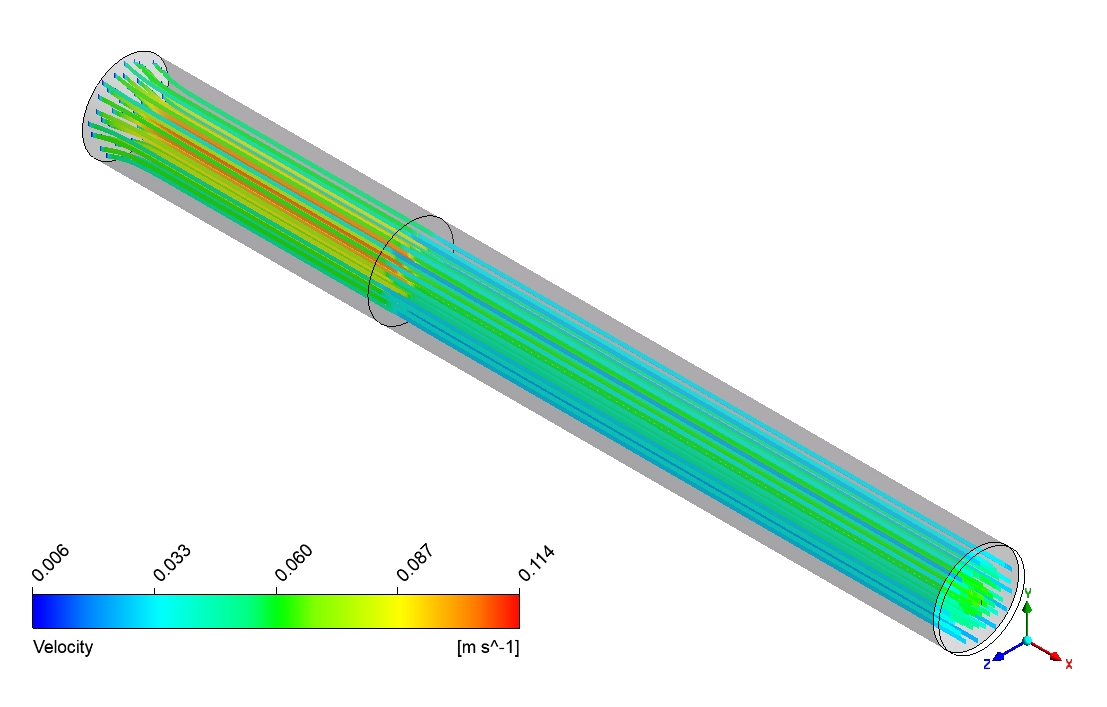
Based on the provided contour plots for the CO2 methanation simulation, we can observe distinct spatial distributions of reactants and products across the reactor. The plot of the reactants reveals regions of elevated concentration adjacent to the inlet, which progressively diminishes as one moves toward the outlet. This gradient illustrates the utilization of CO2 and H2 as they move through the reactor. The steepness of these gradients offers valuable insights into the reaction rate and the catalyst’s efficiency across various reactor regions. The product contour plot for CH4 and H2O demonstrates an inverse pattern, showing that concentrations rise from the inlet to the outlet. This distribution corresponds with the anticipated behavior of the methanation reaction, where products build up as the reactants are utilized. The regions with the greatest product concentration are probably aligned with the most dynamic catalytic zones in the reactor. By analyzing the two contour plots, we can discern areas of maximum reaction efficiency where the consumption of reactants corresponds with the formation of products.
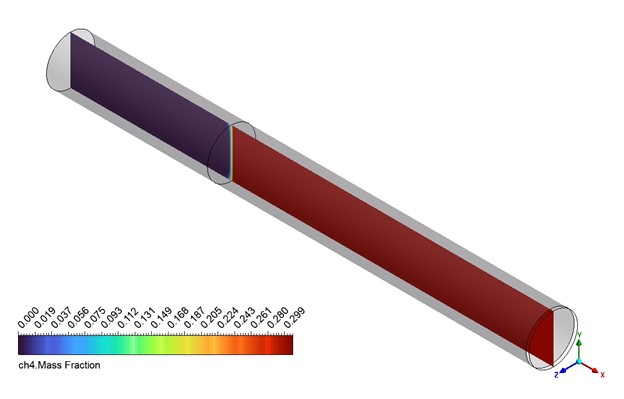
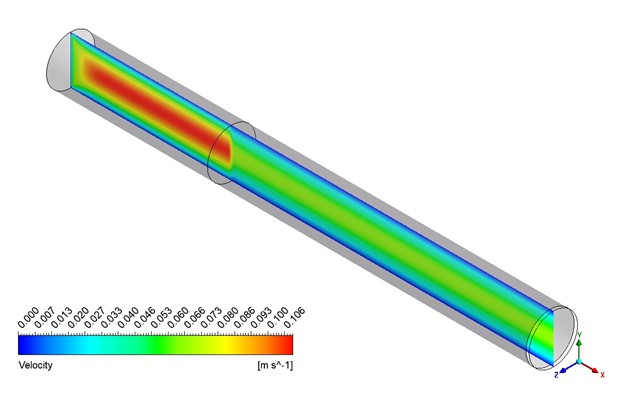
Figure 3: Distribution of a) velocity b) CH4 mass fraction in the reactor through CO2 Methanation CFD Simulation
We pride ourselves on presenting unique products at CFDLAND. We stand out for our scientific rigor and validity. Our products are not based on guesswork or theoretical assumptions like many others. Instead, most of our products are validated using experimental or numerical data from valued scientific journals. Even if direct validation isn’t possible, we build our models and assumptions on the latest research, typically using reference articles to approximate reality.
Yes, we’ll be here . If you have trouble loading files, having technical problems, or have any questions about how to use our products, our technical support team is here to help.
You can load geometry and mesh files, as well as case and data files, using any version of ANSYS Fluent.
€150 Original price was: €150.€130Current price is: €130.

€170 Original price was: €170.€135Current price is: €135.

€380 Original price was: €380.€185Current price is: €185.

€230 Original price was: €230.€145Current price is: €145.

€180 Original price was: €180.€115Current price is: €115.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.