Mixture Transport In Porous Using UDF CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Training
Mixture Transport In Porous Using UDF CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Training
- Upon ordering this product, you will be provided with a geometry file, a mesh file, and an in-depth Training Video that offers a step-by-step training on the simulation process.
- For any more inquiries regarding the product, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at info@CFDLAND.com or through our online support assistant.
€155 Original price was: €155.€135Current price is: €135.
Understanding how fluids move through tiny holes and cracks is super important in today’s engineering world! Mixture transport in porous media represents one of the most challenging problems for engineers who need to predict how different liquids flow through rocks, soil, or industrial filters. When oil and water travel together through sand or special materials, their journey gets complicated because the permeability (how easily fluids can pass) changes from spot to spot. Modern CFD simulation tools like ANSYS Fluent can now solve these tricky problems, but only when enhanced with special code called User Defined Functions (UDF) that tell the computer exactly how the material properties change throughout the space. The fascinating world of multiphase flow in porous structures directly impacts countless real-world applications, from cleaning up dangerous groundwater contamination to maximizing production in valuable oil reservoirs. Moreover, the complex mathematics behind spatial variability of material properties becomes manageable through advanced computational methods that track each drop of fluid as it navigates the twisting paths inside porous materials. Transporting mixtures in porous media with location-dependent permeability is complex due to the porous structure’s spatial variability. This is our ultimate target in the present CFD study.
Simulation Process
A discretized rectangular channel establishes our computational domain, making out of structured grid. The mixture of oil and water plays the main role in which Mixture multiphase model is required. As the title suggests, the porous medium features from location-dependent permeability, known as Viscous Resistance in ANSYS Fluent. Thus, a specific user-defined function (UDF) is written, aiming to apply it. The permeability is governed by the following relation:
![]()
Post-processing
The simulation results show that there are different patterns in velocity and oil distribution within the channel and porous medium. The top picture shows an incredible view of how fast the mixture moves in different spots. We successfully captured the classic parabolic velocity profile that forms when liquids flow through a straight channel. See that bright red streak right down the middle? That’s where the mixture zooms along at its fastest speed (0.460 m/s) – almost half a meter every second! Meanwhile, the blue areas near the walls barely move at all, creating a beautiful speed gradient from edge to center. This happens because the walls grab onto the fluid molecules and slow them down, while the middle molecules can race freely forward. The perfect symmetry of the velocity pattern confirms our simulation is working correctly, and the smooth color transition from blue to red shows how the speed changes gradually rather than suddenly jumping from slow to fast.
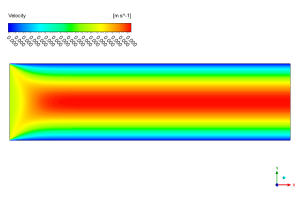
Figure 1: Velocity contour showing fluid flow speed distribution across the rectangular channel
Now check out the amazing oil-water separation in the bottom picture! We perfectly modeled the gravity-driven stratification process that happens when these two liquids flow together through our special porous material. The bright red zones at the top and bottom show where oil (with volume fraction of 0.95) has collected, while the deep blue middle section reveals the water-rich region (with almost zero oil). Notice how the oil layer at the top gets thicker as the mixture moves from left to right? This happens because our UDF creates changing permeability that affects how easily oil can flow in different parts of the channel. Also, look at those thin green-yellow lines between the red and blue areas – that’s the mixing zone where oil and water meet, staying remarkably thin and well-defined throughout the flow. This clean separation proves our simulation correctly handles the physics of how these two fluids interact while flowing through porous material with special properties that change from place to place!
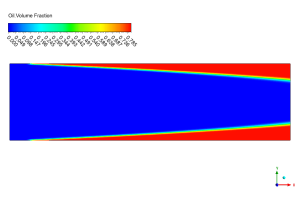
Figure 2: Oil volume fraction contour displaying phase separation between oil
We pride ourselves on presenting unique products at CFDLAND. We stand out for our scientific rigor and validity. Our products are not based on guesswork or theoretical assumptions like many others. Instead, most of our products are validated using experimental or numerical data from valued scientific journals. Even if direct validation isn’t possible, we build our models and assumptions on the latest research, typically using reference articles to approximate reality.
Yes, we’ll be here . If you have trouble loading files, having technical problems, or have any questions about how to use our products, our technical support team is here to help.
You can load geometry and mesh files, as well as case and data files, using any version of ANSYS Fluent.
€310 Original price was: €310.€175Current price is: €175.

€220 Original price was: €220.€125Current price is: €125.

€270 Original price was: €270.€165Current price is: €165.

€360 Original price was: €360.€185Current price is: €185.

€155 Original price was: €155.€99Current price is: €99.

€190 Original price was: €190.€145Current price is: €145.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.