
Nozzle CFD Simulation in ANSYS Fluent: Physics, Types, and Analysis
A nozzle is a very important device in fluid mechanics. It is used to control how fast a fluid moves (velocity) and its pressure. Nozzles

ANSYS Fluent Tutorials & CFD Simulation Training

A nozzle is a very important device in fluid mechanics. It is used to control how fast a fluid moves (velocity) and its pressure. Nozzles
This article explains the difference between validation and verification in scientific modeling and numerical simulation. Many new students and researchers use these two words as
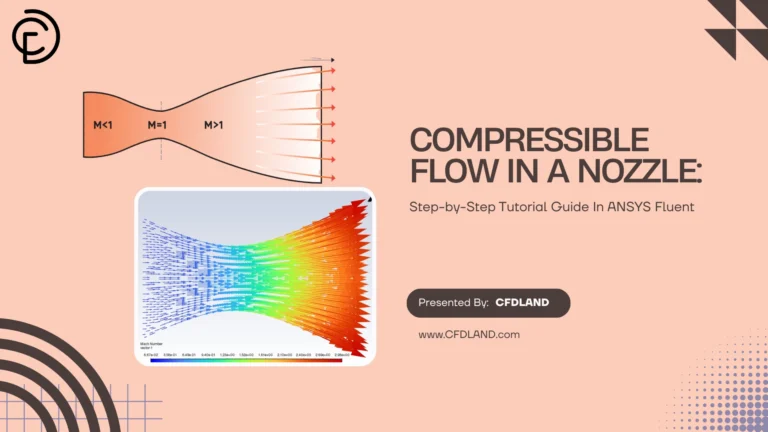
In many engineering systems, fluid can move at low speeds or very high speeds. This creates two important flow types: incompressible flow and compressible flow.

Internal flow is a very important topic in fluid mechanics and engineering. Many systems depend on the movement of liquids and gases inside pipes and

ANSYS Fluent is the world’s leading CFD simulation software. Engineers use it for fluid flow simulation to understand how air, water, and heat move. This

Have you ever wondered what a heat sink does? Simply put, a heat sink is a device that helps keep electronic parts cool. Many devices,

Phase change is a very common physical phenomenon in engineering. It happens when a substance changes its state, like water turning into steam. In Computational
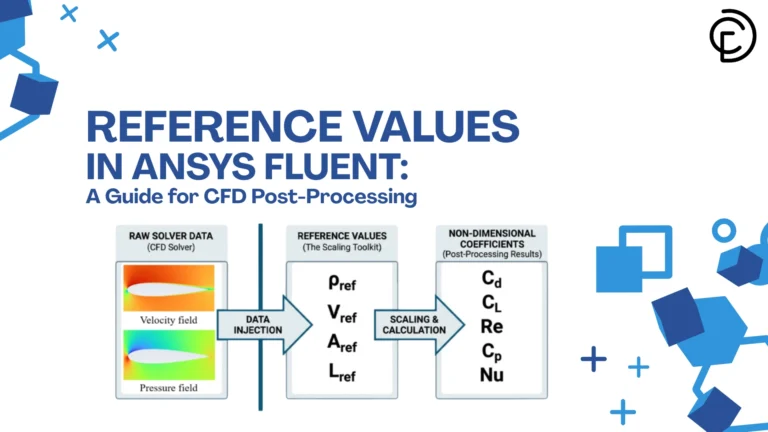
In Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), getting a converged solution is only half the job. To truly understand your results, you need accurate data interpretation. This

An airfoil is a special shape used in wings, blades, and many engineering designs. The curved shape helps control how air moves over the surface.

In ANSYS Fluent, we can model a fan in two main ways. We can use an Internal Fan boundary condition or an External Fan boundary
In every CFD project, you must tell the software what is happening inside your mesh. Is it air? Is it water? Is it a solid
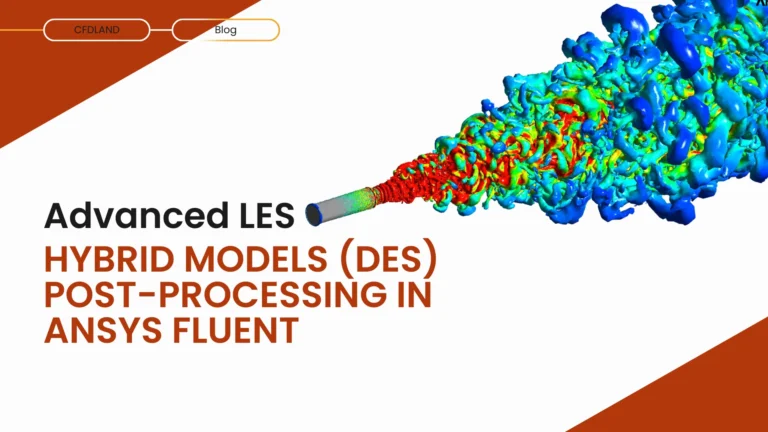
In Blog 2, we set up a complete Large Eddy Simulation (LES) case. We created a high-quality mesh, initialized with RANS, and configured the WALE