
How to Use GPU in ANSYS Fluent?
In computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, achieving faster and more efficient computations is a critical goal for engineers and researchers. With the increasing complexity and

In computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, achieving faster and more efficient computations is a critical goal for engineers and researchers. With the increasing complexity and

2D ANSYS Fluent simulations offer an efficient way to study fluid flow and heat transfer when the third dimension is not significant. If your model’s

Have you ever wondered how to get rid of writing User-Defined Functions (UDFs) in ANSYS Fluent? The good news is that starting from ANSYS 2019
Welcome to the third part of our User-Defined Functions (UDFs) series for ANSYS Fluent! After covering UDF basics and UDF macros in our earlier blogs,
With the rise of electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems, the need for accurate and efficient battery simulation software has never been greater.

In our previous blog post, we introduced the fundamentals of User Defined Functions (UDFs) in ANSYS Fluent. Now, we’ll explore deeper into one of the
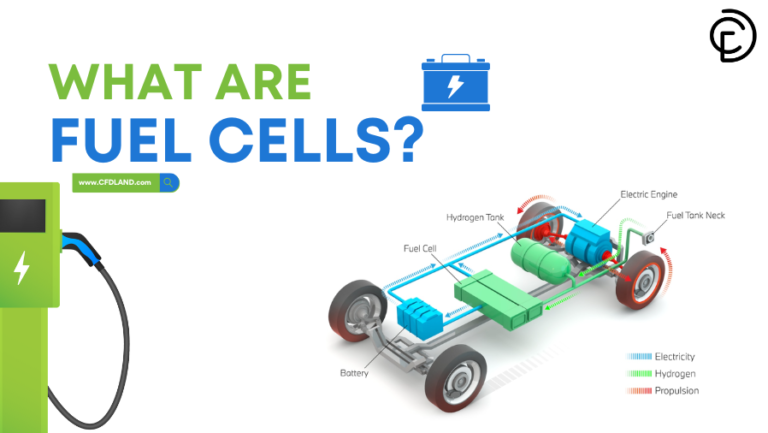
Fuel Cells are cutting-edge electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy directly into electrical energy. Unlike combustion-based systems, they offer high efficiency and low emissions, making
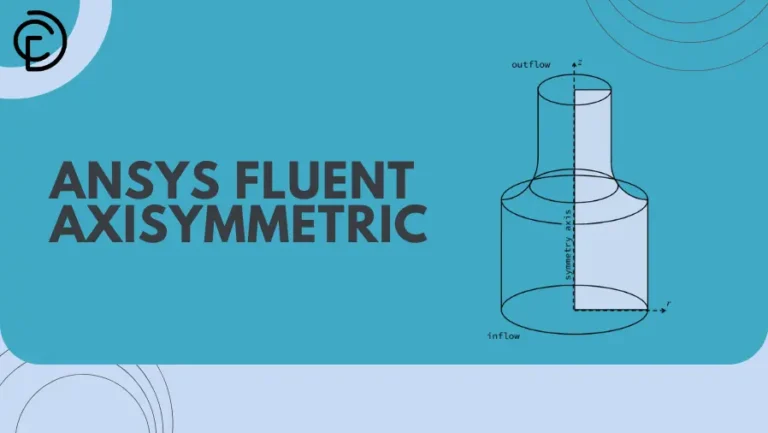
The ANSYS Fluent Axisymmetric modeling approach is a powerful technique used to reduce computational time and resources when dealing with geometries that are symmetric around

User-Defined Functions (UDFs) extend ANSYS Fluent’s capabilities by allowing you to implement custom models and conditions not available in the standard software. This guide introduces

Convergence is a critical aspect of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations, ensuring that the numerical solution obtained is both accurate and reliable. In ANSYS Fluent,

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the Volume of Fluid (VOF) model – one of the most powerful approaches in Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) for
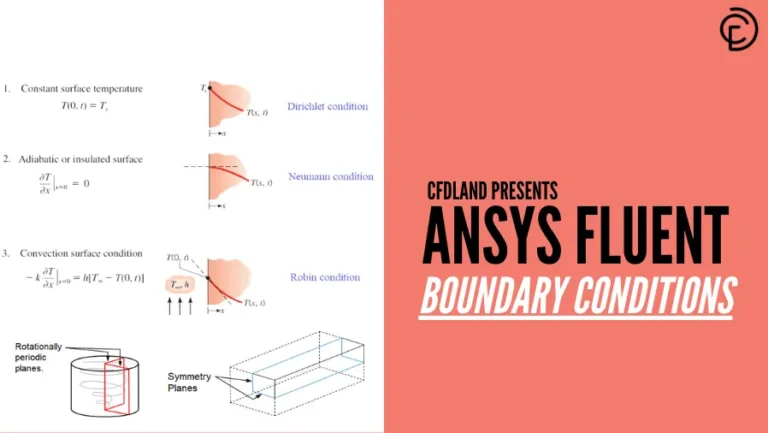
In computational fluid dynamics (CFD), defining proper boundary conditions is essential for accurately solving the governing equations. Boundary conditions in CFD help constrain the discretized