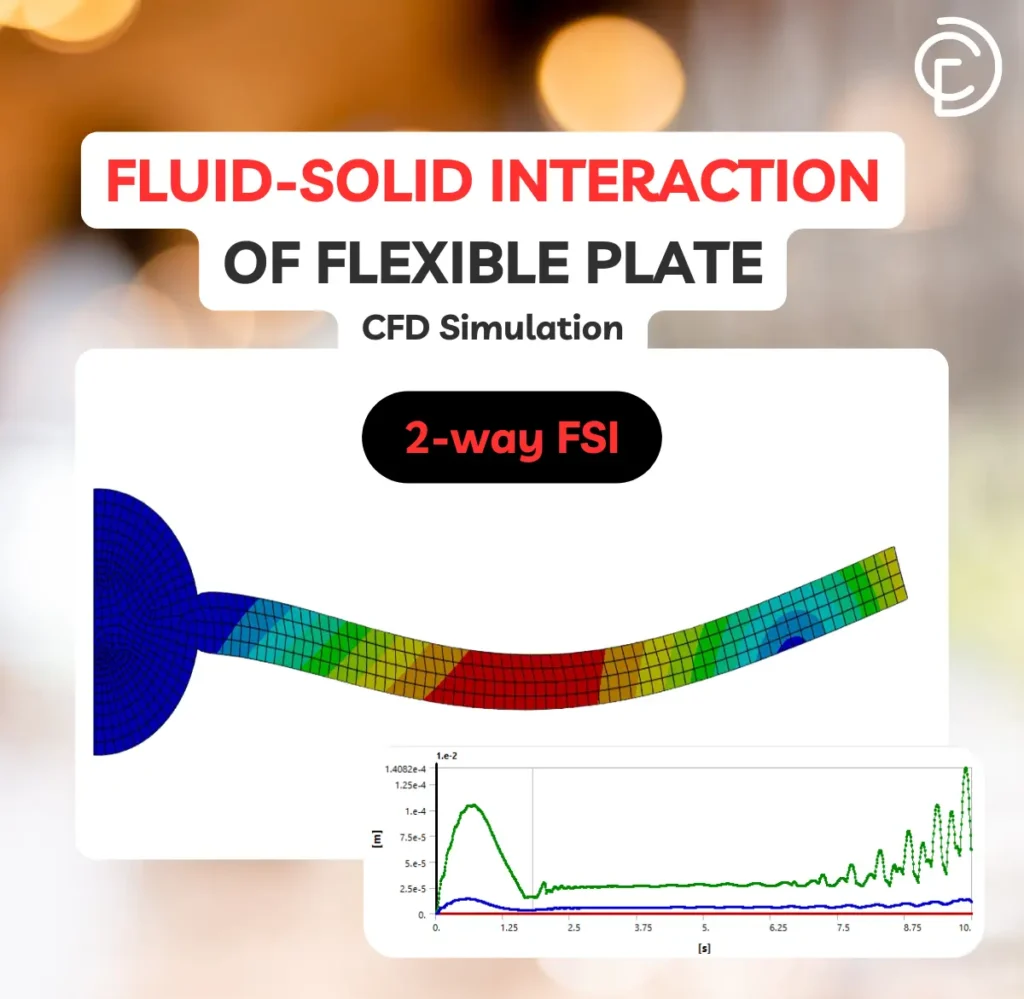
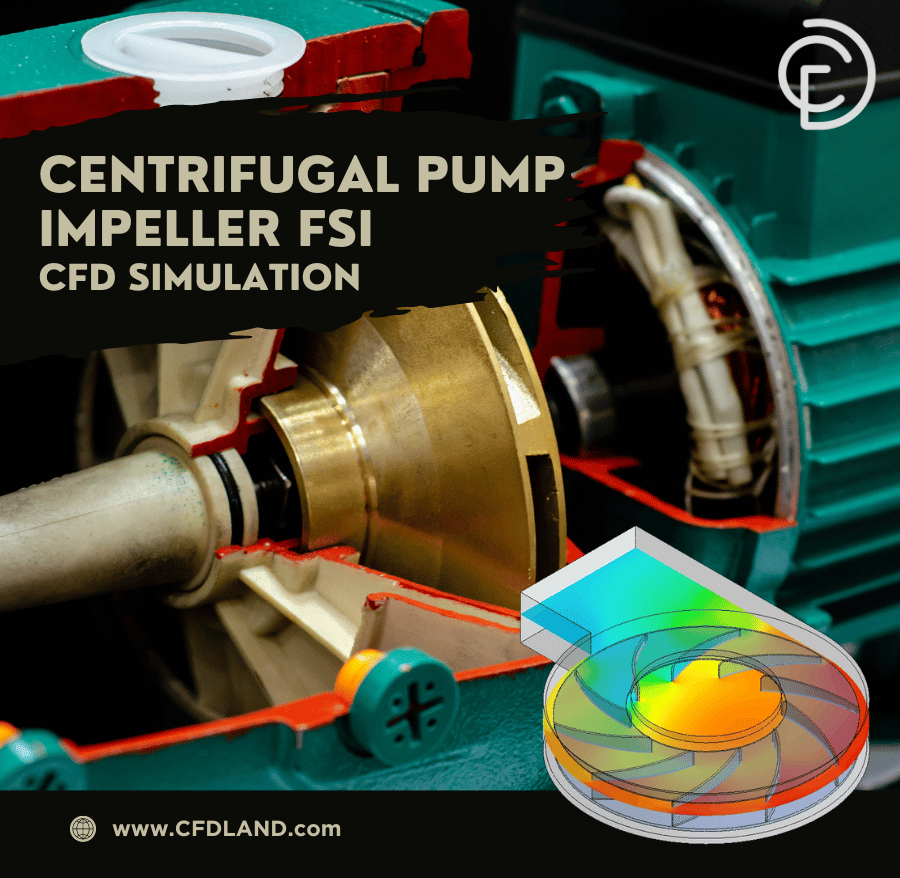
Fluid Structure Interaction
€215 Original price was: €215.€165Current price is: €165.
€205 Original price was: €205.€165Current price is: €165.
€180 Original price was: €180.€155Current price is: €155.
€180 Original price was: €180.€150Current price is: €150.
€185 Original price was: €185.€135Current price is: €135.
Introduction to Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI)
Fluid-Structure Interaction, or FSI, is the study of how fluids and solid objects affect each other. In simple words, it looks at how moving fluids like water or air push on solid parts, and how these parts move or change because of the fluid. This interaction is very important in many fields of engineering and science. For example, when wind flows around a bridge, it pushes on the bridge structure. The bridge can move or vibrate because of the wind. This is a fluid-structure interaction. Engineers need to understand this to make bridges safe and strong.
FSI is also important in machines like pumps and turbines. These machines have parts that move and touch fluids. The way fluids and parts work together affects how well the machine works and how long it lasts. Numerical fluid simulation is a way to study FSI using computers. It helps engineers see what happens inside the fluid and solid parts without making physical models. This saves time and money. ANSYS is one popular software for FSI simulation. It lets engineers model both fluid and solid parts and how they interact.
In this article, we will explain what fluid-structure interaction is, how it works, and how ANSYS software helps in FSI simulations. We will also look at examples and applications. This will help you understand why FSI is important and how it is used in real life.
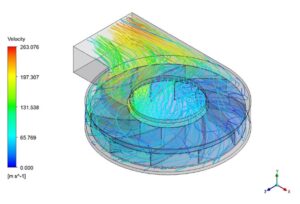
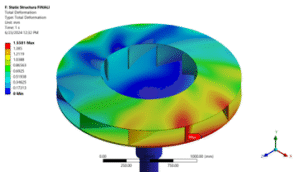
Figure 1: Fluid-Structure Interaction example: The fluid flow pushing the pump blades causes the pump to move.
Basics of Fluid-Solid Interaction
Fluid-Solid Interaction and Fluid-Structure Interaction are two names for the same idea. They both mean the study of how fluids and solid parts work together. In this interaction, the fluid pushes on the solid, and the solid can change shape or move. This change can also affect the fluid flow. Understanding this two-way effect is very important in many engineering problems. There are two main types of fluid solid interaction simulation: one-way and two-way. In one-way fluid-structure interaction, the fluid affects the solid, but the solid does not change the fluid flow. This is simpler and faster to calculate. In two-way fluid-structure interaction, both the fluid and the solid affect each other. This type is more accurate but needs more computing power.
When engineers work on fluid-structure interaction, they use special software. One common software is ANSYS. The fluid solid interaction ANSYS tools allow users to simulate both the fluid and the solid parts together. Another software is COMSOL, which also offers fluid solid interaction simulation. The study of fluid structure interaction helps engineers solve many problems. For example, it is used to check if a bridge can handle wind forces or if a pump’s parts can survive pressure from flowing liquid. Many engineers learn about this in a fluid structure interaction course or use tutorials to improve their skills.
In summary, fluid solid interaction and fluid-structure interaction show how fluids and solids work together. Using software like ANSYS or COMSOL, engineers can simulate this interaction and design safer, better machines and structures.
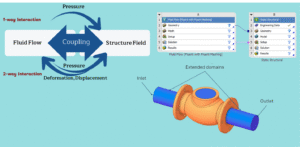
Figure 2: One-way vs. two-way fluid-structure interaction: one-way affects only the solid, two-way affects both fluid and solid.
Numerical Simulation of Fluid-Structure Interaction
Numerical simulation is a way to study fluid-structure interaction using computers. It helps engineers see how fluids and solids behave together without building physical models. This saves time and money and allows testing many designs quickly. In fluid-structure interaction numerical simulation, two main parts work together: fluid flow and solid structure. Engineers use computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to study the fluid part. They use structural analysis to study the solid part. Then, these two parts are connected, or coupled, in the simulation.
There are different methods to connect fluid and solid parts in simulation. One method is called strongly coupled fluid-structure interaction. This means the fluid and solid parts are solved together many times during the simulation. It gives very accurate results but needs more computer power. Another method is called loosely coupled. Here, fluid and solid parts are solved separately and shared less often. This method is faster but less accurate.
Modern software supports these methods. ANSYS is a popular choice for fluid structure interaction simulation. It can handle both CFD and structural parts and connect them for accurate results. Other software like COMSOL also offers fluid solid interaction simulation with multiphysics capabilities.
Using numerical simulation for FSI helps engineers design better machines, buildings, and devices. It is important in fields like aerospace, automotive, and biomedical engineering.
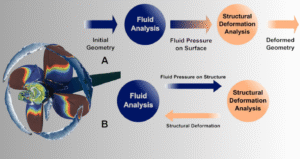
Figure 3: Numerical simulation of fluid-structure interaction shows how fluid flow and solid deformation are connected.
FSI in ANSYS Software
Fluid solid interaction ANSYS tools are very powerful for solving fluid-structure interaction problems. ANSYS software helps engineers simulate how fluids and solids work together. The software can connect fluid flow and solid parts in one environment. This makes it easier to study and design complex systems.
ANSYS Workbench is a popular platform for fluid structure interaction. It combines different solvers for fluid and solid parts. For fluids, ANSYS uses tools like Fluent and CFX. For solid parts, it uses ANSYS Mechanical. These tools work together to perform fluid structure interaction simulation. ANSYS supports both one-way and two-way coupling. This means you can choose simple or detailed models based on your needs. The software also supports strongly coupled fluid-structure interaction for very accurate results. Using ANSYS for FSI helps engineers solve many real problems. For example, they can study how air pushes on airplane wings or how water affects a pump’s parts. The fluid solid interaction simulation in ANSYS is trusted in many industries because it is accurate and reliable.
If you want to learn more, many fluid structure interaction courses include ANSYS training. These courses help users understand how to use ANSYS for FSI problems.
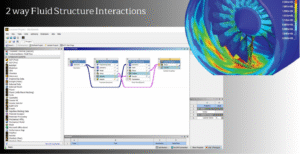
Figure 4: ANSYS Workbench interface showing fluid-structure interaction setup with Fluent and Mechanical solvers.
Understanding Fluid-Solid Coupling
Fluid-solid coupling is a key part of fluid-structure interaction. This process connects fluid flow and solid deformation, allowing engineers to study how forces and motion interact between them. In simulations, data is exchanged between fluid and solid models repeatedly to ensure accuracy. This is called iterative coupling. It helps capture the full interaction of forces, displacements, and pressures in real-world applications.
However, setting up proper coupling can be challenging. Engineers must carefully define the properties of both fluid and solid domains and ensure smooth data transfer. Using tools like ANSYS Workbench, the coupling process becomes easier and more reliable. These tools automatically exchange data between fluid and solid solvers during each step of the simulation.
By understanding fluid-solid coupling, engineers can improve simulation accuracy and study complex systems like bridges, pumps, and airplane wings. This coupling is essential for solving real-world problems where fluid and solid parts interact dynamically.
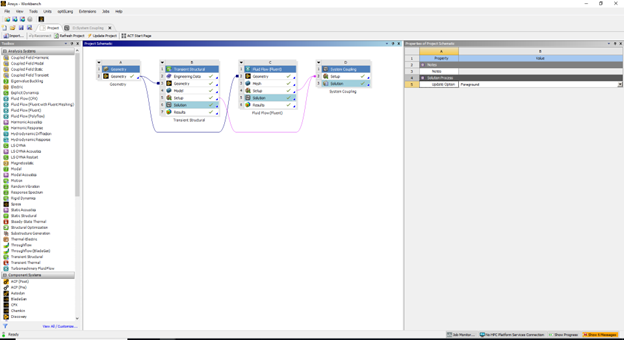
Figure 5: Fluid-solid coupling, Iterative data transfer ensuring accurate results in transient structural and fluid flow simulations.
Defining the Fluid-Solid Interface in Mechanical Environments
The fluid-solid interface is the key area where the fluid and solid domains interact in a simulation. This interface acts as the communication point for forces, pressures, and displacements between the two domains. Properly defining the fluid-solid interface in ANSYS is essential for accurate results in fluid-structure interaction modeling.
In the ANSYS Mechanical environment, engineers use the “Fluid Solid Interface” tool to set up this coupling. This tool allows the user to specify the regions where the fluid and solid interact, ensuring the correct transfer of data like forces from the fluid side and displacements from the solid side. Without this step, the simulation cannot capture the true behavior of the system under study.
The image shows how to define the fluid-solid interface in ANSYS Mechanical. Engineers can select the interface region and configure properties like temperature, pressure, or force conditions. This step is critical for fluid structure interaction analysis, as it connects the physical mechanics of both domains. Proper setup of the interface ensures the simulation runs smoothly and produces reliable results.
By defining the interface carefully, engineers can study complex systems such as bridges under wind loads or pumps where fluid flow interacts with moving components. Accurate definition of this interaction is essential for solving real-world engineering challenges.
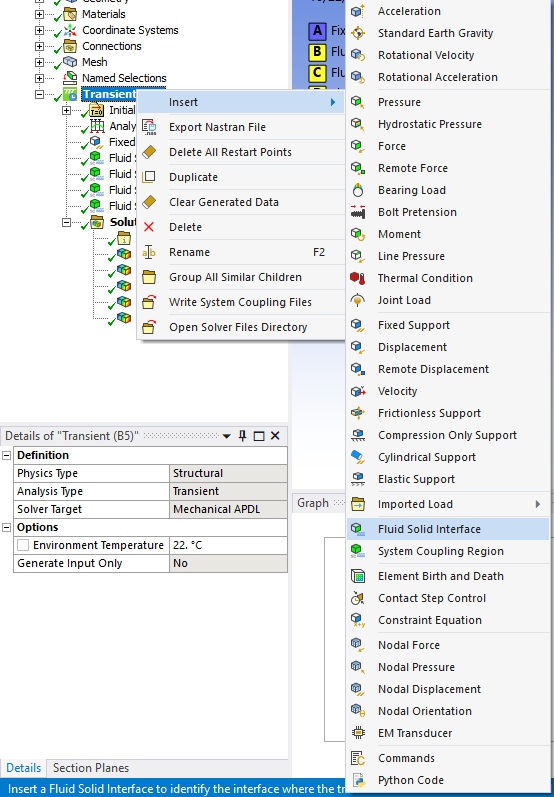
Figure 6: Defining fluid-solid interfaces in ANSYS ensures proper force and motion transfer between fluid and structural environments.
Coupling Systems in ANSYS Fluent
Fluid-solid coupling systems are essential for solving fluid-structure interaction simulations. In ANSYS Fluent, coupling systems connect fluid and solid domains, allowing them to interact dynamically during simulations. This image shows the dynamic mesh zones used in ANSYS Fluent to manage the motion of solid boundaries interacting with fluid flow. These mesh zones are critical for ensuring smooth data transfer between fluid and solid systems during the coupling process.
The System Coupling option in Fluent is used to define how fluid and solid domains exchange information. Engineers can specify different types of motion for mesh zones, such as deforming or stationary, depending on the physical behavior of the system. For example, in a pump simulation, the rotating blades (solid domain) deform the fluid flow, and Fluent dynamically adjusts the mesh to account for this interaction.
By using dynamic mesh zones and system coupling, engineers can simulate real-world systems where fluid and solid components interact in complex ways. This process ensures accurate results for applications such as turbine design, biomedical devices, or structural systems subjected to fluid forces. Fluent’s fluid solid interaction analysis tools provide flexibility and precision in defining coupling systems, saving time and improving the reliability of simulations.
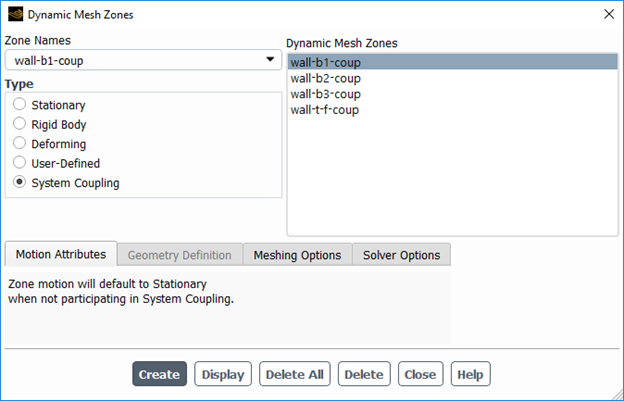
Figure 7: The system coupling setup in ANSYS Workbench simplifies fluid-solid interaction simulation with dynamic meshing capabilities.
Fluid-Solid Coupling Data Exchange: Iterative Process
The Figure 9 illustrates the iterative process of fluid-solid coupling in simulations. It displays the data transfer between fluid flow (Fluent) and transient structural components, emphasizing how the two domains interact dynamically. This diagram represents the changes in Root Mean Square (RMS) values during multiple coupling iterations, ensuring the simulation achieves convergence and stability.
In fluid-structure interaction modeling, the coupling process is crucial for transferring forces, displacements, and pressures between the fluid and solid systems. The red curve represents the data transfer from the fluid flow domain, while the green curve represents the data from the transient structural domain. The fluctuations visible in the graph reflect how the system adjusts during each iteration to balance the interaction forces and achieve accurate results.
The iterative nature of fluid-solid coupling ensures that the simulation captures the real-world dynamics of complex systems, such as the behavior of a bridge under wind loads or a pump operating with fluid flow. Engineers rely on tools like ANSYS Fluent coupling systems to configure this interaction effectively. By monitoring the RMS values in the coupling diagram, they can evaluate the performance of their simulation and make necessary adjustments to achieve accurate outcomes.
Understanding this diagram is vital for fluid structure interaction analysis, as it demonstrates the importance of maintaining a stable, two-way data exchange between fluid and solid domains. Without proper coupling, the simulation may fail to capture the true physical behavior of the system, resulting in unreliable results.
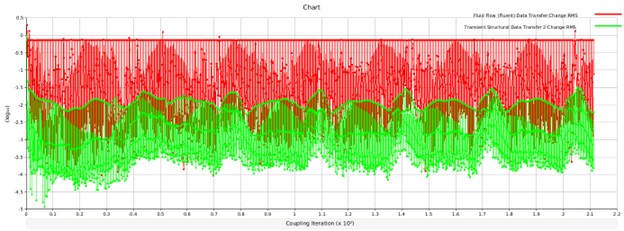
Figure 9: The coupling diagram shows iterative data exchange between fluid flow (red) and transient structural domains (green) for achieving convergence and stability in fluid-solid simulations.
Other FSI Software (e.g., COMSOL)
Besides ANSYS, there are other important software tools used for fluid solid interaction and fluid-structure interaction. One popular option is COMSOL, which also offers strong fluid solid interaction simulation features with excellent multiphysics capabilities. Both ANSYS and COMSOL help engineers study how fluids and solids work together by linking fluid flow and solid deformation in one model. These software tools are widely used in industry and research to solve complex engineering problems where fluid and structure affect each other.
Choosing between ANSYS and COMSOL depends on the specific project needs and the user’s experience. Many engineers improve their skills by taking a fluid structure interaction course that covers both software platforms. This training helps them decide which tool to use for different types of FSI problems. Both software packages support fluid-structure interaction multiphysics and are trusted by engineers worldwide to design safer and more efficient products. In summary, fluid solid interaction ANSYS and fluid solid interaction COMSOL stand as two top software options, each with its own strengths in the field of fluid-structure interaction simulation.
- ANSYS is best for detailed fluid and structural simulations with high accuracy, especially in industrial applications.
- COMSOL excels in flexible multiphysics setups and is easier for beginners or research users focused on coupled physics problems.
Applications of Fluid-Structure Interaction
Fluid-structure interaction is very important in many areas of engineering and science. Understanding how fluids and solids work together helps engineers design safer and better products. The study of fluid-structure interaction applications covers many fields, such as aerospace, biomedical engineering, and mechanical systems.
In aerospace, fluid-structure interaction helps analyze how air flows around airplane wings and how the wings move because of this flow. This knowledge is very important to avoid problems like wing flutter, which can be dangerous. Engineers use fluid-structure interaction in aerospace to make aircraft safer and more efficient.
In biomedical engineering, fluid-structure interaction is used to study blood flow inside arteries. Blood is a fluid, and artery walls are solid. By simulating this interaction, doctors and engineers can better understand diseases and design medical devices. This is a key example of fluid-structure interaction in biomedical engineering.
Mechanical systems like pumps and turbines also rely on fluid-structure interaction. These machines have parts that move and contact fluids constantly. Simulating the fluid solid interaction helps engineers improve the design, performance, and lifespan of these machines.
Overall, fluid-structure interaction engineering plays a big role in solving real-world problems. Using software like ANSYS, engineers can perform detailed fluid solid interaction simulation to study these applications and create better designs that are safer, stronger, and more efficient.
Figure 10: Fluid-Structure Interaction applications in aerospace, biomedical engineering, and mechanical systems.
Fluid-structure interaction (FSI) is a complex but essential area of engineering that connects fluid dynamics with solid mechanics. Its applications span across industries, from energy and aerospace to biomedical devices and marine engineering. Understanding FSI requires not only knowledge of numerical methods but also hands-on experience with tools like ANSYS Fluent coupling systems and Workbench environments. CFDLand provides an excellent platform for engineers and researchers to learn, explore, and apply FSI concepts through its diverse range of products and completed projects.
CFDLand offers a unique opportunity for learners and professionals to dive deep into fluid-solid interaction analysis. The site’s products are designed to simplify the process of mastering fluid-solid coupling by providing pre-configured simulations and tutorials. These resources are ideal for anyone looking to develop expertise in numerical simulation of fluid-structure interaction.
Some of the key learning products include:
- Wind Turbine Acoustics Simulation: A two-way fluid-solid coupling tutorial that focuses on optimizing turbine designs by studying aeroacoustic effects and energy efficiency.
- Sloshing FSI Analysis: A simulation of fluid behavior within an oil tanker, showcasing how fluid-solid interaction modeling supports safe ship designs under dynamic loads.
- Wave CFD Simulation: This tutorial examines offshore column vibration under wave loads, providing insights into marine engineering applications.
- Human Eye FSI Simulation: A biomedical-focused tutorial exploring how fluid flow interacts with the iris and aqueous humor in the human eye.

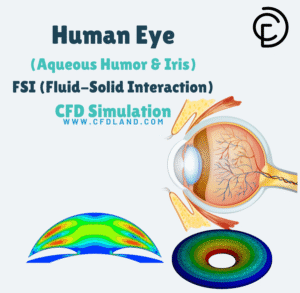


Figure 11: numerical simulation of fluid-structure interaction, CFDLANAD FSI tutorials in ANSYS Fluent.
Alongside these products, CFDLand’s completed projects give users real-world examples of FSI applications. For instance:
- Flexible Plate FSI Analysis: A project that uses two-way fluid-solid coupling to study plate deformation under fluid flow.
- Heat Press Machine Analysis: A detailed simulation of thermal and mechanical interaction in industrial equipment, solving complex engineering challenges.
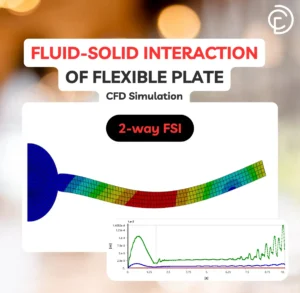

Figure 12: Real-world examples of FSI applications, CFDLANAD FSI tutorials.
These resources demonstrate the versatility of fluid structure interaction analysis and how it can be applied to improve safety, efficiency, and innovation across various sectors.
Conclusion
Fluid-structure interaction modeling is transforming engineering by allowing simulation and design of systems that respond to fluid forces in real-time. The iterative process of fluid-solid coupling, as seen in simulation diagrams, ensures accurate results and helps engineers solve complex problems like turbine blade deformation, bridge vibration, and medical device optimization.
CFDLand’s products and projects bridge the gap between theory and real-world practice. By using detailed tutorials and pre-configured simulation files for ANSYS Fluent coupling systems and Workbench environments, learners move from basic understanding to advanced problem-solving. These resources make it possible to master the numerical simulation of fluid-structure interaction at your own pace, with clear examples and expert support.
Engineers who use CFDLand gain practical knowledge and confidence to tackle FSI challenges. They can create safer, more efficient, and innovative designs for industries around the world. Whether you are starting out or looking to advance your expertise, CFDLand provides the tools and training you need for success in fluid-solid interaction analysis.